
Vikram Engineering IPO GMP: Day-3 Subscription & Investor Outlook
Vikram Engineering IPO GMP is trending among investors, with strong subscription numbers on Day 3. This blog explores GMP trends, subscription status, and whether the IPO is worth applying for.
Table of Contents
Introduction: Overview of Vikram Engineering’s Public Offering
Vikram Engineering Limited concluded its initial public offering on August 29, 2025, attracting substantial attention from market participants across multiple investor categories. The offering, valued at ₹772 crores, represents a significant capital-raising exercise in India’s engineering services sector.
The company’s public offering concluded with a subscription level of 23.59 times the shares offered. This response indicates considerable investor interest in the engineering services segment. The subscription period spanned from August 26 to August 29, 2025, with allocation finalized on September 1, 2025, and listing scheduled for September 3, 2025, on both BSE and NSE.
This analysis examines the IPO structure, subscription data, grey market indicators, company fundamentals, and sector positioning. The objective is to provide factual information based on official disclosures and market data.
IPO Structure and Financial Details
Issue Composition and Capital Allocation
Vikram Engineering’s IPO comprises two distinct components as per SEBI guidelines. The fresh issue component amounts to ₹721 crores, involving 7.43 crore shares. This portion represents new equity capital that will be deployed for business operations. The Offer for Sale (OFS) component totals ₹51 crores, consisting of 0.53 crore shares from existing shareholders.
The price band was set between ₹92 and ₹97 per share. At the upper price band of ₹97, the total issue size reached ₹772 crores. The minimum application lot was fixed at 148 shares, requiring a minimum investment of ₹14,356 for retail investors.
Use of Proceeds and Deployment Strategy
According to the company’s Red Herring Prospectus filed with SEBI, the fresh issue proceeds are earmarked for specific purposes. Capital will be allocated toward working capital requirements, debt repayment, and general corporate purposes. The engineering services sector typically requires substantial working capital for project execution, materials procurement, and contract management.
The OFS component allows existing promoters to partially divest their holdings while maintaining majority control. This structure balances growth capital needs with shareholder liquidity objectives.
Registration and Regulatory Framework
The IPO was registered with the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) under the applicable regulations. BigShare Services Private Limited serves as the registrar for the issue, handling application processing, allotment, and refund procedures. Link Intime India Private Limited was appointed as the share transfer agent.
Subscription Performance Analysis
Day-wise Subscription Progression
The subscription window opened on August 26, 2025, following anchor investor allocation on August 25, 2025. Day one witnessed steady application inflow across investor categories. By the close of the first day, initial subscription figures indicated positive market reception.
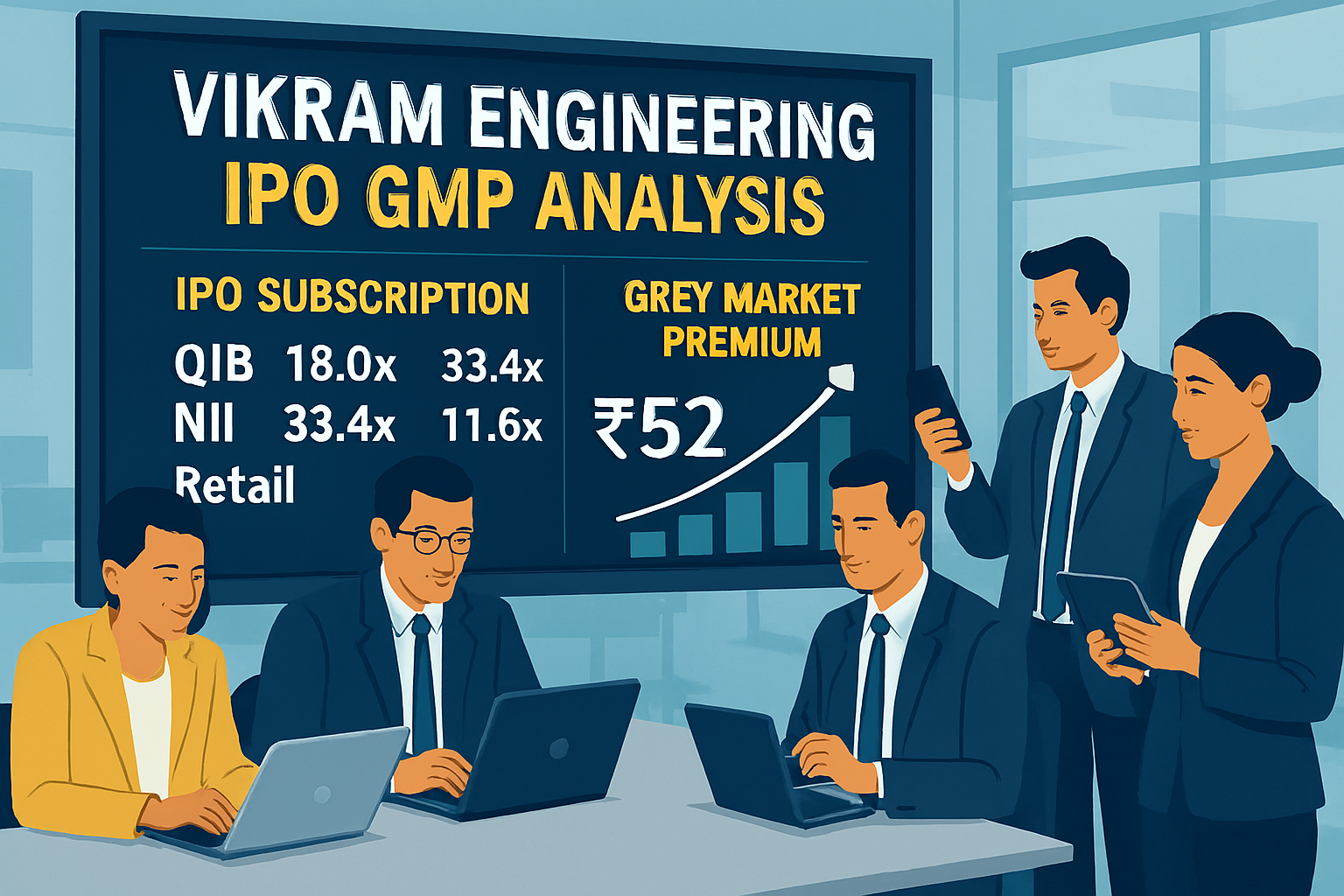
On the second day, August 28, 2025, subscription levels reached 5.52 times. Non-institutional investors (NIIs) subscribed to 11.63 times their allocated portion, while retail individual investors (RIIs) subscribed 5.52 times. This acceleration demonstrated increasing interest as the subscription period progressed.
The final day, August 29, 2025, concluded with overall subscription reaching 23.59 times. This represented a significant increase from day two levels, indicating concentrated application submission on the closing day.
Category-wise Subscription Breakdown
According to data from stock exchange filings, different investor categories demonstrated varying levels of participation. The qualified institutional buyers (QIBs) category, comprising mutual funds, insurance companies, and foreign portfolio investors, showed measured participation. This segment typically evaluates fundamental factors and long-term value propositions.
Non-institutional investors, including high net worth individuals with application values exceeding ₹2 lakhs, subscribed over 11 times during the subscription period. This category often responds to short-term listing potential and market momentum factors.
Retail individual investors, with application values up to ₹2 lakhs, demonstrated strong participation. This segment benefits from reserved allocation quotas under SEBI guidelines, ensuring proportionate distribution even in oversubscribed offerings.
Anchor Investor Participation
Anchor investors were allocated shares on August 25, 2025, one day before the public offering opened. This category comprises institutional investors who receive allocation at the discovered price before retail subscription begins. The anchor book provides an indication of institutional confidence and helps price discovery.
Details of anchor investor allocation, including names of participating institutions and allocation amounts, are disclosed in the post-anchor investor allocation report filed with stock exchanges. This information is publicly available through BSE and NSE websites.
Grey Market Premium Analysis
Understanding Grey Market Dynamics
The grey market operates as an unofficial secondary market for IPO shares before listing. Participants trade application rights or expected allotments based on perceived listing potential. While not regulated by SEBI, grey market trends often indicate investor sentiment.
According to market sources, Vikran Engineering’s grey market premium (GMP) stood at ₹21 per share as of August 26, 2025. This suggests an estimated listing price of ₹118, representing a premium of approximately 21.65% over the upper price band of ₹97. However, grey market quotations fluctuate based on market conditions and should be interpreted cautiously.
GMP Fluctuations During Subscription Period
Grey market premiums typically vary throughout the subscription period based on application flow and overall market sentiment. Reports indicate the GMP reached a high of ₹25 on August 21, 2025, and a low of ₹5 on September 2, 2025. This volatility reflects changing expectations regarding listing performance.
Higher GMP levels generally correlate with strong subscription numbers and positive market sentiment. However, grey market indications do not guarantee actual listing performance. Multiple factors, including overall market conditions on listing day, sector sentiment, and institutional buying patterns, influence opening prices.
Limitations of Grey Market Data
Investors should note that grey market data lacks official verification and regulatory oversight. Quotations vary across different grey market operators. The informal nature of these transactions means price discovery may not accurately reflect actual demand-supply dynamics at listing.
SEBI does not recognize grey market transactions, and participants bear counterparty risks. Historical data shows instances where actual listing prices diverged significantly from grey market indications, both positively and negatively.
Company Profile and Business Operations
Business Model and Service Offerings
Vikran Engineering Limited operates in the engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) sector. The company provides integrated engineering solutions across infrastructure, industrial, and construction segments. Services encompass design, engineering, procurement, construction, and project management.
The company’s operations span multiple sectors including infrastructure development, industrial facilities, power projects, and commercial construction. This diversification provides revenue stability across different economic cycles and sector-specific demand patterns.
Project Portfolio and Execution Track Record
According to company disclosures, Vikran Engineering has completed 45 projects across various sectors. Additionally, 44 projects are currently under execution. This pipeline provides near-term revenue visibility and demonstrates the company’s capacity to manage multiple concurrent projects.
Project completion records indicate the company’s ability to meet contractual obligations, maintain quality standards, and adhere to delivery timelines. These factors influence client retention and repeat business opportunities in the competitive EPC sector.
Geographic Presence and Market Positioning
The company operates primarily within India, serving clients across different states and regions. Geographic diversification helps mitigate regional economic fluctuations and provides access to multiple project opportunities. The ability to execute projects in diverse locations demonstrates operational flexibility and resource management capabilities.
Market positioning within the fragmented Indian EPC sector depends on factors including technical expertise, financial stability, execution track record, and client relationships. Established players compete based on specialization, pricing, and delivery reliability.
Financial Performance Overview
Revenue Model and Recognition
EPC companies typically recognize revenue using the percentage of completion method for long-term contracts. This accounting treatment matches revenue recognition with project progress, measured through cost incurred or physical completion milestones. Revenue patterns tend to be project-dependent, creating quarterly variations.
The business model requires substantial working capital for mobilization advances, material procurement, and operational expenses before receiving client payments. Cash flow management becomes critical, particularly during rapid growth phases with multiple ongoing projects.
Cost Structure and Margin Dynamics
Engineering services companies face cost pressures from raw material price fluctuations, labor costs, equipment rental charges, and subcontractor expenses. Margin sustainability depends on efficient project estimation, cost control during execution, and contract negotiation capabilities.
Competitive bidding environments can compress margins, particularly for standardized projects where differentiation opportunities are limited. Companies maintain profitability through operational efficiency, project selection, and value engineering.
Working Capital Requirements
The EPC sector typically operates with extended working capital cycles. Companies advance funds for mobilization, materials, and execution before receiving progress payments from clients. Retention money is often held back until project completion and warranty periods conclude.
Efficient working capital management involves negotiating favorable payment terms, optimizing inventory levels, managing receivables, and maintaining supplier relationships. Bank financing through working capital loans and bank guarantees supports operational requirements.
Sector Analysis: Engineering and Construction Industry
Industry Size and Growth Trajectory
India’s engineering and construction sector contributes significantly to GDP and employment generation. The sector encompasses infrastructure development, industrial projects, commercial construction, and residential building. Government initiatives and private sector investments drive demand for engineering services.
According to reports from industry associations and government ministries, infrastructure spending continues to increase. National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) projects, Smart Cities Mission, industrial corridor development, and renewable energy installations create opportunities for engineering companies.
Key Growth Drivers
Infrastructure development remains a government priority, with budget allocations increasing for roads, highways, railways, ports, and airports. State governments and municipal corporations also undertake infrastructure projects, expanding the addressable market for EPC companies.
Industrial sector expansion, driven by manufacturing initiatives and capacity additions, generates demand for plant construction, facility development, and specialized engineering services. Sectors including steel, cement, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and automotive require engineering expertise for greenfield and brownfield projects.
Competitive Landscape
The Indian EPC sector includes large national players, mid-sized regional companies, and numerous small contractors. Competition intensity varies across project types, with large infrastructure projects dominated by established players having financial capacity and execution capabilities.
Differentiation occurs through technical specialization, sector focus, geographic concentration, and client relationships. Companies develop expertise in specific domains such as power, water, transportation, or industrial construction. This specialization enables competitive advantages in technical execution and project bidding.
Sector Challenges and Risk Factors
Engineering companies face several operational challenges. Project delays due to land acquisition issues, environmental clearances, and regulatory approvals impact execution timelines and profitability. Changes in material prices during long-duration projects affect margin realization if contracts lack price escalation clauses.
Client payment delays and disputes create cash flow pressures. Working capital intensity increases during rapid growth, requiring bank financing and impacting financial leverage ratios. Competition for contracts leads to aggressive bidding, potentially compromising margins.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance Framework
SEBI IPO Guidelines
Initial public offerings in India are governed by SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2018. These regulations prescribe eligibility criteria, disclosure requirements, issue procedures, pricing mechanisms, and allotment processes. Companies must meet profitability or net worth criteria for accessing public markets.
The regulations mandate reservation quotas for different investor categories: retail individual investors (up to 35%), non-institutional investors (at least 15%), and qualified institutional buyers (up to 50%). Oversubscription in any category leads to proportionate allotment as per prescribed formulas.
Exchange Listing Requirements
Companies listing on BSE and NSE must comply with listing agreements and continuous disclosure obligations. These include quarterly financial results, annual reports, material event notifications, and corporate governance requirements. Minimum public shareholding of 25% must be maintained as per regulatory norms.
Listed companies follow accounting standards prescribed by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI). Financial statements undergo audit by qualified auditors before submission to exchanges. Corporate actions require board and shareholder approvals as per Companies Act provisions.
Sector-specific Regulations
Engineering and construction companies operate within regulatory frameworks governing environmental compliance, labor laws, safety standards, and quality certifications. Project execution requires various statutory clearances from central and state authorities.
Environmental impact assessments are mandatory for certain project categories. Pollution control boards monitor compliance with environmental norms. Labor laws govern employee welfare, safety measures, and contractual arrangements for project-specific workforce deployment.
Allotment Process and Timeline
Application Verification and Processing
After the subscription period closes, the registrar compiles application data from stock exchanges, self-certified syndicate banks (SCSBs), and syndicate members. Applications undergo verification for technical correctness, fund availability, and duplicate detection. Invalid applications are rejected, and funds are unblocked or refunded.
The basis of allotment is finalized in consultation with stock exchanges. For oversubscribed categories, proportionate allotment follows SEBI guidelines. Retail investors receive minimum one lot if applications exceed available shares, with remaining shares allotted proportionately. Successful applicants receive share allocation to their demat accounts.
Allotment Status Verification
Investors can check allotment status through the registrar’s website, BigShare Services Private Limited. The process requires entering PAN number, application number, or demat account details. Stock exchange websites (BSE and NSE) also provide allotment status verification facilities.
Allotment for Vikran Engineering IPO was finalized on September 1, 2025. Investors receiving allocation had shares credited to their demat accounts before listing. Those not receiving allocation or receiving partial allocation had funds unblocked or refunded within prescribed timelines.
Refund Mechanisms
SEBI regulations mandate refund processing within a specified timeframe after allotment finalization. For applications through UPI and net banking, funds remain blocked in investor accounts and are unblocked automatically for unsuccessful allotments. For ASBA applications through cheques, refunds are initiated to registered bank accounts.
The registrar coordinates with banks and clearing systems to ensure timely refund processing. Any delays beyond prescribed timelines attract interest payments to affected investors as per SEBI guidelines.
Listing Expectations and Price Discovery
Factors Influencing Listing Performance
Multiple factors affect IPO listing prices on debut day. Overall market sentiment, sector-specific trends, subscription levels, and institutional buying interest influence opening price discovery. Broader market indices (Nifty, Sensex) movement on listing day impacts investor sentiment toward new listings.
Company-specific factors include financial performance, growth prospects, competitive positioning, and management quality. Valuation metrics relative to listed peers affect institutional investor interest. Strong fundamentals may attract long-term investors, supporting post-listing price stability.
Historical Listing Patterns
Historical data from previous IPOs provides context for expectations. Highly oversubscribed issues with strong grey market premiums often witness positive listing gains. However, correlation is not absolute, and exceptions occur based on market conditions and sector sentiment.
Mid-cap IPOs in the engineering sector have shown varied listing performance historically. Some delivered significant listing gains, while others listed at par or discount to issue price. Investor sentiment toward the infrastructure and construction sector influences new issue reception.
Post-listing Price Trajectory
Listing day performance does not necessarily predict medium-term price movement. Initial euphoria may lead to profit booking by short-term investors seeking listing gains. Subsequent price discovery depends on fundamental performance, quarterly results, order book announcements, and sector trends.
Long-term price appreciation correlates with revenue growth, profitability improvement, and market share expansion. Companies meeting or exceeding market expectations typically witness sustained investor interest. Operational challenges, project delays, or margin compression can pressure valuations.
Investment Considerations for Different Investor Profiles
Short-term Trading Perspective
Investors seeking listing gains focus on subscription levels, grey market premium trends, and debut day price momentum. Strong oversubscription and positive GMP suggest potential listing gains. However, this approach carries risks if market sentiment shifts or profit booking pressure exceeds buying interest.
Trading strategies include booking partial or full profits on listing day, depending on premium achieved. Setting realistic profit targets based on grey market indications helps avoid excessive optimism. Stop-loss levels protect against adverse price movements if listings disappoint expectations.
Medium-term Investment Approach
Investors with 1-3 year horizons evaluate company fundamentals alongside listing potential. Financial performance trajectory, order book growth, execution capabilities, and sector trends become relevant. Valuation metrics such as price-to-earnings, price-to-book, and enterprise value multiples guide investment decisions.
Medium-term success depends on the company meeting growth expectations through consistent project wins, timely execution, and margin maintenance. Quarterly result announcements and order inflow updates provide performance feedback. Sector developments and infrastructure spending trends influence medium-term outlook.
Long-term Value Investment
Long-term investors prioritize sustainable competitive advantages, management quality, financial discipline, and sector positioning. Business model resilience across economic cycles, ability to generate consistent returns on capital, and prudent capital allocation distinguish quality companies.
Evaluating management track record, corporate governance standards, and stakeholder treatment helps assess long-term value creation potential. Companies with strong balance sheets, efficient working capital management, and profitable growth merit premium valuations.
Risk Analysis Framework
Company-specific Operational Risks
Project execution risks include cost overruns, timeline delays, quality issues, and contractual disputes. Engineering companies must accurately estimate project costs, manage subcontractors, and maintain quality control. Underestimation leads to margin erosion, while delays trigger penalty clauses.
Client concentration risk arises when significant revenue derives from limited customers. Loss of major clients or project cancellations impacts revenue and profitability. Diversification across clients, sectors, and geographies mitigates this risk.
Financial and Liquidity Risks
Working capital intensity creates cash flow pressures, particularly during growth phases. Extended payment cycles, retention money, and bank guarantee requirements strain liquidity. Companies may require debt financing, increasing financial leverage and interest costs.
Debt levels affect financial flexibility and credit ratings. High leverage reduces capacity for additional borrowing when opportunities arise. Interest coverage ratios and debt service obligations require monitoring. Companies with efficient working capital management and moderate leverage exhibit lower financial risk.
Market and Sector Risks
Economic slowdowns reduce infrastructure spending and industrial project activity. Government fiscal constraints impact public sector project allocations. Regulatory changes, policy shifts, and approval delays affect project execution timelines.
Raw material price volatility impacts project profitability, especially for fixed-price contracts without escalation clauses. Labor availability, particularly skilled technical personnel, affects execution capabilities. Intense competition compresses margins and reduces pricing power.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks
Engineering projects require numerous statutory clearances from environmental, pollution control, and local authorities. Delays in obtaining approvals postpone project commencement and revenue recognition. Non-compliance with labor laws, safety regulations, or environmental norms triggers penalties and reputation damage.
Changes in tax structures, GST rates, or accounting standards impact financial reporting and profitability. Companies must maintain robust compliance frameworks and legal expertise to navigate regulatory complexities.
Peer Comparison and Valuation Benchmarking
Identifying Comparable Companies
Peer group selection involves identifying listed companies with similar business models, revenue scales, and market positioning. Mid-sized EPC companies operating in infrastructure, industrial, and construction segments form relevant peer sets. Companies with comparable project portfolios and geographic presence enable meaningful comparison.
Financial Metrics Comparison
Key metrics for comparison include revenue growth rates, operating margins, net profit margins, return on equity, and debt-to-equity ratios. Higher growth rates reflect expanding market share and successful project wins. Superior margins indicate operational efficiency and pricing power.
Return on capital employed measures how effectively companies utilize capital to generate profits. Efficient working capital management reduces capital intensity and improves returns. Debt levels relative to equity and operating profits indicate financial leverage and repayment capacity.
Valuation Multiples Analysis
Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios reflect market expectations regarding earnings growth. Companies with strong growth prospects typically command premium P/E multiples. Price-to-book (P/B) ratios compare market value to book value, indicating whether stocks trade at premium or discount to accounting values.
Enterprise value-to-EBITDA multiples assess total valuation relative to operating performance before depreciation and interest. This metric facilitates comparison across companies with different capital structures. Sector average multiples provide context for individual company valuations.
Macroeconomic Factors and Industry Outlook
Government Infrastructure Initiatives
Central government infrastructure programs significantly impact EPC sector demand. National Infrastructure Pipeline allocates substantial funds across sectors including transportation, energy, water, and urban development. Budget announcements detail infrastructure spending commitments and project pipelines.
Smart Cities Mission, AMRUT (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation), and PM Gati Shakti initiatives create engineering services opportunities. State governments implement complementary infrastructure programs, expanding addressable markets for regional and national players.
Private Sector Capital Expenditure
Industrial sector capacity expansions generate demand for plant construction and engineering services. Manufacturing initiatives encourage companies to establish or expand production facilities. Sectors including automobiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and electronics undertake periodic capital expenditure cycles.
Commercial real estate development in Tier-1 and Tier-2 cities requires construction and engineering expertise. Office complexes, retail spaces, hospitality projects, and institutional buildings provide revenue streams for EPC companies. Healthcare and education infrastructure modernization creates additional opportunities.
Technological Advancements
Construction technology evolution includes prefabrication, modular construction, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and automation. Companies adopting these technologies achieve efficiency gains, cost optimization, and quality improvements. Digital project management tools enhance coordination and timeline adherence.
Sustainable construction practices incorporating green building certifications and energy-efficient designs gain prominence. Engineering companies developing expertise in sustainable construction access premium segments and environmentally conscious clients.
Corporate Governance and Management Assessment
Board Composition and Independence
Corporate governance standards influence investor confidence and long-term value creation. Board composition, including independent director representation, ensures balanced decision-making and stakeholder interest protection. Independent directors provide strategic guidance and oversight without management or promoter conflicts.
Audit committees, nomination and remuneration committees, and stakeholder relationship committees ensure transparency and compliance. Regular board meetings, documented decision-making processes, and adherence to governance codes demonstrate organizational maturity.
Management Experience and Track Record
Management team experience in the engineering and construction sector affects operational capabilities and strategic decision-making. Promoter backgrounds, educational qualifications, and industry tenure provide insights into leadership quality. Previous project execution records indicate management competence.
Succession planning, professional management integration, and talent retention strategies ensure organizational continuity. Companies transitioning from promoter-driven to professionally managed structures require careful evaluation of management depth and systems.
Related Party Transactions
Related party transactions require disclosure and independent director approval under regulatory frameworks. Significant transactions with promoter entities, group companies, or management relatives demand scrutiny for fairness and commercial rationale. Transparent disclosure practices and arm’s length pricing demonstrate governance commitment.
Expert Opinions and Analyst Views
Brokerage Research Reports
Securities firms publish research reports analyzing IPOs from fundamental and valuation perspectives. Reports assess financial performance, business model sustainability, competitive positioning, and growth prospects. Recommendation ratings (subscribe, avoid, or neutral) guide investor decision-making.
Analysts evaluate issue pricing relative to earnings, peer valuations, and growth expectations. Price targets based on discounted cash flow models, comparable company analysis, or sum-of-the-parts valuations provide benchmarks. However, brokerage recommendations should be considered alongside personal research and risk assessment.
Independent Market Commentary
Financial media platforms feature expert commentary on IPO opportunities and risks. Industry consultants, former corporate executives, and independent analysts provide diverse perspectives. Commentary addresses sector dynamics, company-specific factors, and macroeconomic influences.
Investor forums and social media discussions reflect retail investor sentiment. While these platforms generate awareness, information verification through official sources remains essential. Speculative discussions without factual basis should be discounted.
Tax Implications for IPO Investors
Capital Gains Tax Structure
Listed equity securities held for more than 12 months qualify as long-term capital assets. Long-term capital gains exceeding ₹1.25 lakh annually attract 12.5% tax without indexation benefits (as of current tax laws). Gains up to ₹1.25 lakh are exempt.
Short-term capital gains (holding period up to 12 months) are taxed at 20%. Securities Transaction Tax (STT) is charged on equity transactions, making gains eligible for beneficial capital gains tax treatment. Investors should consult tax advisors for personalized guidance.
Dividend Distribution Tax
Listed companies distribute dividends to shareholders from post-tax profits. Dividend income is taxable in recipients’ hands as per applicable income tax slabs. TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) is applicable on dividend payments exceeding specified thresholds.
Documentation Requirements
Investors must maintain records of allotment details, purchase price, and holding period for tax filing purposes. Demat account statements and contract notes serve as transaction evidence. Capital gains computation requires accurate cost basis determination and systematic recordkeeping.
Post-listing Monitoring Framework
Quarterly Results Analysis
Listed companies publish quarterly financial results including revenue, operating profit, net profit, and earnings per share. Comparing actual performance against analyst estimates and prior year figures indicates business momentum. Commentary in results presentations provides management perspectives on performance drivers.
Key metrics for monitoring include revenue growth trends, margin stability, order book status, and cash flow generation. Deviations from expectations require understanding underlying causes and assessing whether they represent temporary challenges or structural issues.
Order Book and Pipeline Updates
EPC companies periodically disclose order book status representing contracted future revenue. Order inflow and execution rates indicate demand trends and operational efficiency. Diversification across clients, sectors, and geographies within order books reduces concentration risks.
New order announcements, project wins, and contract renewals demonstrate market competitiveness. Large project wins provide revenue visibility but may increase execution risk and working capital requirements.
Corporate Actions and Announcements
Material events require disclosure to stock exchanges within specified timeframes. Announcements regarding acquisitions, capacity expansions, fund raising, management changes, or strategic partnerships affect investment theses. Investors should review these disclosures for implications on business direction and financial structure.
Annual general meetings provide forums for shareholder interaction with management. Annual reports contain detailed financial statements, management discussion and analysis, and corporate governance disclosures. These documents facilitate comprehensive company evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What was the final subscription status of Vikram Engineering IPO?
The Vikram Engineering IPO concluded with an overall subscription of 23.59 times the shares offered. The subscription period ran from August 26 to August 29, 2025. Different investor categories showed varying subscription levels, with non-institutional investors subscribing over 11 times during the period. This subscription data is available through official stock exchange filings and registrar reports.
When is the Vikram Engineering IPO listing date?
Vikram Engineering shares are scheduled to list on both BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) and NSE (National Stock Exchange) on September 3, 2025. The allotment was finalized on September 1, 2025. Listing schedules are subject to regulatory approvals and stock exchange clearances. Investors can verify listing dates through official exchange websites and company announcements.
What is the grey market premium for Vikram Engineering IPO?
According to market sources, the grey market premium (GMP) was reported at ₹21 per share as of August 26, 2025. This suggested an estimated listing price around ₹118 based on the upper price band of ₹97. However, grey market quotations are unofficial, unregulated, and fluctuate based on market sentiment. They do not guarantee actual listing performance. Investors should not rely solely on grey market indications for investment decisions.
How can investors check Vikram Engineering IPO allotment status?
Allotment status can be verified through BigShare Services Private Limited, the official registrar for the issue. Investors need to enter their PAN number, application number, or demat account details on the registrar’s website. Alternatively, BSE and NSE websites provide allotment status checking facilities. Mobile applications and broker platforms also offer allotment verification services. Status becomes available after allotment finalization on September 1, 2025.
What is the minimum investment amount for Vikram Engineering IPO?
The minimum application lot size was 148 shares. At the upper price band of ₹97 per share, the minimum investment required was ₹14,356. Retail investors can apply for up to 13 lots (1,924 shares) totaling approximately ₹1,86,628. Applications above ₹2 lakhs fall under the non-institutional investor category with different allotment processes.
What are the key business segments of Vikram Engineering?
Vikram Engineering operates in the engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) sector across multiple segments. The company provides services for infrastructure development projects, industrial construction and engineering, power sector solutions, water treatment systems, and commercial construction support. According to company disclosures, 45 projects have been completed with 44 projects currently under execution across these segments.
What are the main risks associated with investing in Vikram Engineering IPO?
Key investment risks include project execution challenges such as cost overruns and timeline delays, working capital management requirements typical of EPC businesses, client concentration risks if revenue depends on limited customers, and sector-specific factors like economic sensitivity and regulatory changes. Additionally, competitive pricing pressures in the engineering sector and raw material price volatility can impact profitability. Investors should carefully evaluate these risks against potential returns.
How does Vikram Engineering compare with listed peers in the sector?
Peer comparison requires evaluating companies with similar business models in the engineering and construction sector. Key comparison metrics include revenue growth rates, operating margins, return on equity, and debt-to-equity ratios. Valuation multiples such as price-to-earnings and enterprise value-to-EBITDA ratios relative to sector averages indicate whether valuations are at premium or discount. Investors should review detailed financial disclosures and analyst research for comprehensive peer comparisons.
About the Author
Nueplanet is a financial markets analyst with theyears of experience covering equity markets, IPO analysis, and sector research. Specializing in infrastructure and engineering sectors, Nueplanet provides data-driven analysis based on official regulatory filings, company disclosures, and authoritative market sources.
Commitment: All content is researched using verified sources including SEBI filings, stock exchange data, company Red Herring Prospectuses, and official announcements. Analysis aims to present factual information enabling informed investor decision-making.
About This Publication
This financial news platform is committed to providing accurate, transparent, and timely information on stock market developments, IPO analysis, and sector trends. Content is based on official sources including regulatory filings, stock exchange announcements, and verified market data.
Editorial Standards:
- All information verified through primary sources before publication
- Regular content updates to reflect latest developments
- Clear distinction between factual reporting and analytical commentary
- No promotional relationships with companies covered
- Commitment to balanced, objective financial journalism
Publish Date: August 29, 2025
Last Updated: August 29, 2025
Disclaimer
This content is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute investment advice, financial recommendations, or solicitation to buy or sell securities. Readers should conduct independent research and consult qualified financial advisors before making investment decisions.
Past performance and subscription success do not guarantee future results. All investments carry inherent risks including potential loss of principal. The author and publication are not registered investment advisors. Information is based on sources believed to be reliable but accuracy cannot be guaranteed.
Readers should review official company documents, SEBI filings, and stock exchange disclosures before investing. Market conditions change rapidly and information may become outdated. Investment decisions remain the sole responsibility of individual investors.






















Post Comment