
Paradeep Phosphates Share Price: Q1 FY26 Surge & Outlook for 2025–26
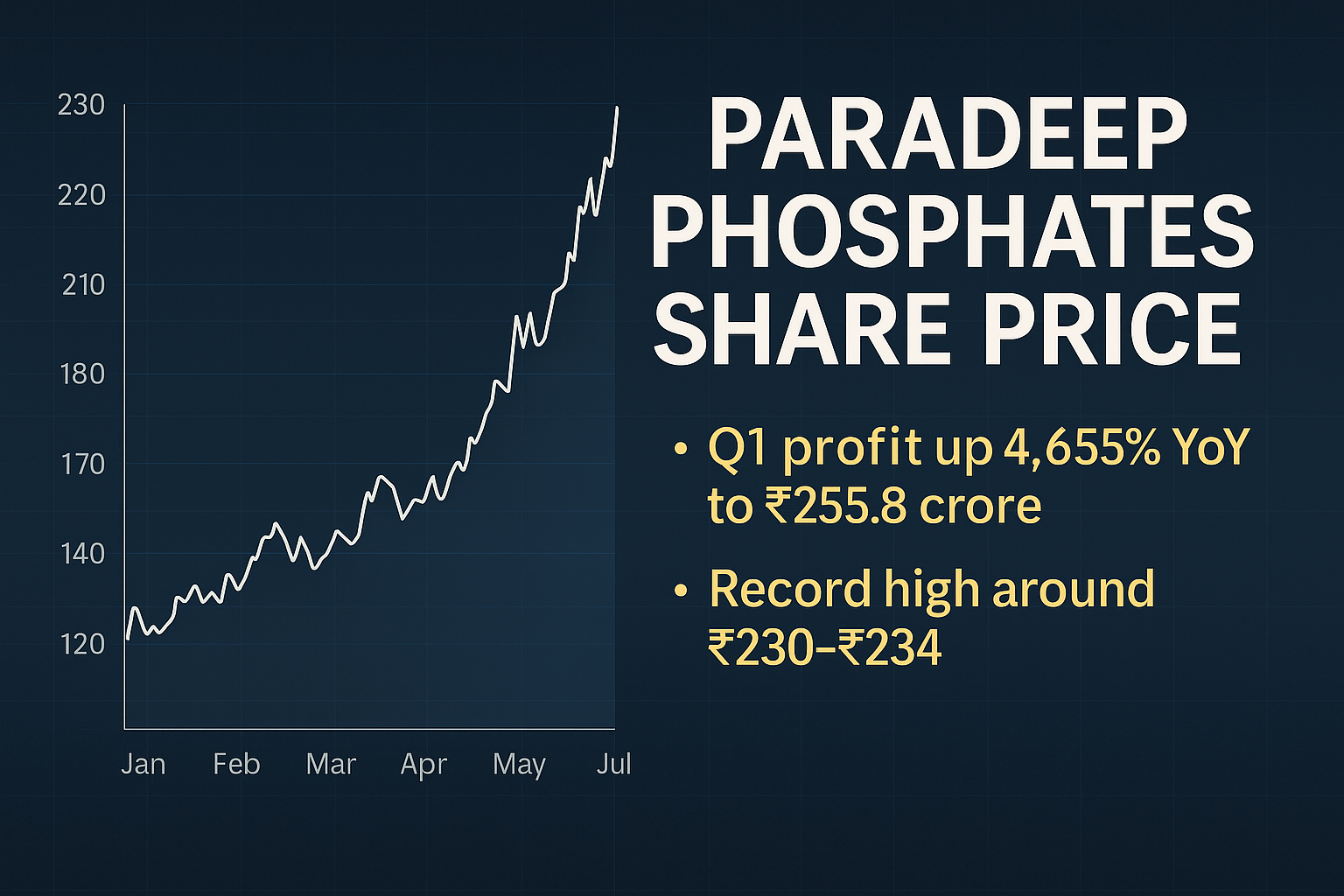
Paradeep Phosphates delivered a staggering 4,655% YoY net profit surge to ₹255.8 crore in Q1 FY26, propelling its share price to record highs around ₹230–₹234. As investor sentiment peaks, we analyze performance drivers, valuation, and what lies ahead
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
Paradeep Phosphates Limited reported its financial results for the first quarter of fiscal year 2026 (April-June 2025), showing significant year-over-year improvements in key financial metrics. The company, which operates as a major producer of phosphatic fertilizers in India’s private sector, announced consolidated net profit of ₹255.8 crore for the quarter ended June 30, 2025. This represented substantial growth compared to ₹5.4 crore in the corresponding quarter of the previous fiscal year.
Revenue from operations reached ₹3,754 crore during Q1 FY26, marking growth from ₹2,377 crore in Q1 FY25. The company’s EBITDA for the quarter stood at ₹466 crore, compared to ₹147 crore in the year-ago period. Following the results announcement, the company’s shares traded in the range of ₹227-₹234 on both BSE and NSE exchanges.
This analysis examines the quarterly financial performance, stock price movements, sector dynamics, and various factors affecting the company’s operations based on publicly available financial data and regulatory filings.
Company Background and Business Operations
Corporate Profile
Paradeep Phosphates Limited operates manufacturing facilities for phosphatic fertilizers at locations in Paradeep, Odisha, and Zuari Nagar, Goa. The company’s product portfolio includes Di-ammonium Phosphate (DAP), various grades of NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium) fertilizers, and specialty agricultural inputs. The company markets its products under the “Navratna” brand across multiple states in India.
As a private sector participant in India’s fertilizer industry, the company operates within a regulatory framework that includes government subsidy programs for agricultural inputs. The fertilizer sector in India involves coordination between manufacturers, government agencies, and distribution networks to ensure product availability during critical agricultural seasons.
Manufacturing Infrastructure
The company’s production facilities are strategically located near port infrastructure, facilitating raw material imports and finished product distribution. Manufacturing operations involve processing phosphoric acid, ammonia, and other inputs into finished fertilizer products. Capacity utilization rates and operational efficiency directly impact production costs and profitability margins.
The Paradeep facility in Odisha and the Zuari Nagar facility in Goa together provide the company’s total production capacity for phosphatic fertilizers. Both locations have access to transportation infrastructure including ports, railways, and road networks for logistics operations.
Q1 FY26 Financial Performance Analysis
Profit and Loss Statement Review
Net Profit Performance
The consolidated net profit of ₹255.8 crore in Q1 FY26 compared to ₹5.4 crore in Q1 FY25 represents the headline figure from the quarterly results. This change reflects various factors including revenue growth, margin improvements, and operational efficiency measures implemented by the company. Financial analysts typically examine such year-over-year comparisons to assess business trajectory and operational performance trends.
However, quarter-to-quarter comparisons in the fertilizer industry require consideration of seasonal factors, monsoon patterns, and agricultural cycles that influence demand. Single-quarter results should be evaluated within the context of full-year performance and multi-year trends to understand sustainable profitability levels.
Revenue Analysis
Revenue from operations of ₹3,754 crore in Q1 FY26 versus ₹2,377 crore in Q1 FY25 indicates growth in the company’s top-line performance. Revenue changes in the fertilizer sector can result from multiple factors including sales volume variations, product pricing adjustments, product mix changes, and subsidy payment timing.
The fertilizer industry in India operates with government subsidies on certain products, affecting revenue recognition and realization patterns. Companies report revenue based on sales to dealers and distributors, with subsidy components either included in revenue or recognized separately depending on accounting treatments.
EBITDA and Margin Analysis
EBITDA Performance
EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) of ₹466 crore in Q1 FY26 compared to ₹147 crore in Q1 FY25 reflects operational profitability before certain non-cash expenses and financial charges. EBITDA serves as a proxy for operating cash generation capacity and helps assess core business profitability independent of capital structure and tax considerations.
The EBITDA margin of 12.4% in Q1 FY26 versus 6.2% in Q1 FY25 indicates the relationship between operating profits and revenue. Margin expansion can result from various factors including economies of scale, input cost management, product pricing improvements, or favorable product mix shifts. Sustained margin improvements over multiple quarters provide stronger evidence of structural profitability enhancement versus temporary favorable conditions.
Cost Structure Considerations
Fertilizer manufacturing involves significant raw material costs for inputs like phosphoric acid, ammonia, sulphuric acid, and other chemicals. Global commodity price fluctuations for these inputs directly impact manufacturing costs. Companies manage input cost volatility through procurement strategies, inventory management, and operational efficiency measures.
Other operating costs include employee expenses, power and fuel costs, freight and distribution expenses, and administrative overheads. The relationship between fixed and variable costs affects operational leverage, where revenue increases can generate disproportionate profit improvements if fixed costs remain stable.
Stock Price Movement and Trading Activity
Post-Results Price Action
Following the Q1 FY26 results announcement, Paradeep Phosphates shares traded in a range between ₹227 and ₹234 on BSE and NSE exchanges. Market participants evaluate quarterly results against expectations and prior performance to determine appropriate valuation adjustments. Stock price movements reflect collective market assessment of earnings quality, sustainability, and future prospects.
Trading volumes typically increase around results announcements as investors and traders react to disclosed financial information. Price volatility during such periods can exceed normal trading ranges as participants process new information and adjust positions accordingly.
Historical Price Trends
Stock price performance over extended periods provides context for evaluating current valuations. The shares had traded at various levels in preceding months based on multiple factors including company-specific developments, sector trends, and broader market conditions. Historical price patterns help identify support and resistance levels that may influence future trading.
Technical analysts examine price charts, moving averages, volume patterns, and momentum indicators to identify trends and potential turning points. Fundamental analysts focus on financial metrics, valuation ratios, and business performance to assess intrinsic value relative to market prices.
Market Capitalization Assessment
Based on the trading range of ₹220-₹230 per share and the company’s outstanding share count, the market capitalization approximated ₹17,900 crore. Market capitalization represents the total value that public market investors assign to a company’s equity. This metric enables comparisons with sector peers and assessment of relative size within industry segments.
Companies with market capitalizations between ₹5,000 crore and ₹20,000 crore typically fall within the mid-cap category in Indian equity markets. Mid-cap stocks generally exhibit different risk-return characteristics compared to large-cap or small-cap segments, with potentially higher growth prospects balanced against greater volatility.
Valuation Metrics and Financial Ratios
Price-to-Earnings Ratio Analysis
The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio compares a company’s share price to its earnings per share, providing a measure of how much investors pay for each rupee of earnings. At the prevailing price range and based on recent earnings, the P/E ratio approximated 22-23 times. This metric enables comparison with industry peers and historical valuation ranges.
P/E ratios vary across sectors and companies based on growth expectations, business quality, competitive positioning, and market conditions. Fertilizer companies historically traded at different valuation multiples depending on factors including subsidy policy frameworks, raw material cost cycles, and agricultural demand trends.
Investors should note that P/E ratios based on quarterly earnings may not reflect sustainable annual earnings capacity. Full-year earnings provide more reliable bases for valuation assessment given seasonal variations in the fertilizer business.
Return on Equity Assessment
Return on Equity (ROE) measures profitability relative to shareholders’ equity, indicating how efficiently a company generates profits from invested capital. The three-year average ROE of approximately 14.4% provides perspective on historical profitability trends. ROE analysis should consider whether returns exceed the cost of equity capital and how returns compare to industry benchmarks.
Sustained high ROE can indicate competitive advantages, effective capital allocation, or favorable industry dynamics. However, ROE interpretation requires consideration of leverage levels, as companies with higher debt-to-equity ratios may show inflated ROE figures that don’t reflect underlying business quality.
Price-to-Book Ratio Evaluation
The Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio compares market capitalization to book value of equity, providing perspective on how much premium investors pay over accounting book value. A P/B ratio around 4 times indicates that the market values the company at four times its net asset value per books.
P/B ratios above 1.0 suggest that investors believe the company can generate returns exceeding its cost of capital. Companies with strong market positions, efficient operations, and growth prospects typically trade at premiums to book value. However, P/B ratios should be evaluated considering accounting policies, asset quality, and intangible value factors not captured on balance sheets.
Sector Context and Industry Dynamics
Fertilizer Industry Structure in India
India’s fertilizer sector comprises both public and private sector manufacturers, with government involvement through subsidy programs and policy frameworks. The sector serves the agricultural industry, which employs a significant portion of India’s population and contributes substantially to GDP. Fertilizer availability and affordability directly impact agricultural productivity and farmer economics.
The industry faces periodic challenges related to raw material import dependence, subsidy payment delays, and regulatory complexity. Phosphatic fertilizers like those produced by Paradeep Phosphates contain phosphorus nutrients essential for crop development. Demand patterns follow agricultural cycles and monsoon seasonality.
Government Policy Framework
The Government of India implements subsidy programs for various fertilizer categories to ensure affordability for farmers. The Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) scheme applies to phosphatic and potassic fertilizers, providing fixed subsidy rates per nutrient. Companies receive subsidies from the government based on sales volumes and applicable rates.
Policy changes regarding subsidy rates, import duties, or regulatory requirements can significantly impact industry economics. The fertilizer sector requires ongoing monitoring of policy developments announced by the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers and related government agencies.
Agricultural Demand Factors
Fertilizer demand correlates with agricultural activity levels, which depend on monsoon patterns, crop prices, farmer income levels, and credit availability. The 2025 monsoon season’s progression affects Kharif (summer) crop planting and associated fertilizer consumption. Normal or above-normal monsoons typically support agricultural activity and fertilizer demand.
Government initiatives promoting balanced nutrient application and soil health management influence fertilizer product mix and consumption patterns. Awareness about micronutrient deficiencies has increased demand for specialty products beyond traditional NPK fertilizers.
Competitive Landscape Assessment
Private Sector Participants
India’s phosphatic fertilizer segment includes several private sector producers competing on manufacturing efficiency, distribution reach, product quality, and service delivery. Companies with integrated facilities, modern technology, and effective supply chains maintain competitive advantages. Market positioning depends on factors including production capacity, geographical presence, and brand recognition.
Competition intensity varies across regions and product categories. Some companies focus on specific fertilizer grades while others maintain diversified portfolios. Distribution network strength significantly influences market access and customer relationships in the fragmented agricultural retail environment.
Public Sector Presence
Public sector fertilizer companies operate under different ownership structures and policy mandates compared to private companies. Some public sector entities receive specific government support or operate under different financial parameters. The public-private sector mix affects overall industry dynamics and competitive intensity.
Paradeep Phosphates competes with both private and public sector entities across various markets and product categories. Competitive positioning reflects operational efficiency, cost management, product quality, and service delivery capabilities.
International Competition and Imports
India imports significant quantities of phosphatic fertilizers and raw materials for domestic manufacturing. Import policies, customs duties, and trade agreements affect domestic industry economics. International price trends for finished fertilizers and raw materials influence domestic market conditions.
Companies with efficient operations and favorable cost structures maintain better positioning during periods of international price volatility. The balance between domestic production and imports shifts based on price competitiveness, policy frameworks, and logistical considerations.
Operational Performance Factors
Manufacturing Efficiency Indicators
Capacity utilization rates measure how effectively companies use installed production capacity. Higher utilization rates typically improve per-unit fixed cost allocation and overall cost competitiveness. Operational efficiency also depends on plant reliability, maintenance practices, and process optimization.
Energy consumption per unit of production represents a key efficiency metric in fertilizer manufacturing. Companies invest in energy efficiency improvements to reduce operating costs and environmental impact. Process technology, equipment condition, and operational practices all influence energy efficiency levels.
Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management affects both cost structure and service delivery capabilities. Procurement strategies for raw materials impact input costs and inventory carrying requirements. Logistics efficiency for finished product distribution influences delivery costs and customer service levels.
Seasonal demand patterns require careful inventory planning to ensure product availability during peak consumption periods while managing working capital requirements. Companies balance inventory costs against stock-out risks that could result in lost sales opportunities.
Quality Control and Product Differentiation
Fertilizer product quality affects crop response and customer satisfaction. Companies implement quality control processes throughout manufacturing to ensure products meet specifications. Laboratory testing, process monitoring, and quality assurance systems maintain consistency.
Some companies differentiate through specialty products, customized formulations, or value-added services beyond commodity fertilizer offerings. Product innovation and technical support can support premium pricing or customer loyalty advantages.
Risk Factors and Considerations
Monsoon and Weather Dependency
Agricultural activity in India depends heavily on monsoon rainfall patterns, which vary annually in timing, distribution, and intensity. Deficient or delayed monsoons reduce agricultural activity and fertilizer demand. While irrigation coverage has expanded, significant agricultural areas remain monsoon-dependent.
Climate variability and extreme weather events represent ongoing risks for agricultural inputs sectors. Companies cannot control weather factors but can manage exposure through diversified geographic presence, flexible operations, and appropriate financial planning.
Raw Material Price Volatility
Phosphoric acid, ammonia, and other raw materials represent major cost components in phosphatic fertilizer manufacturing. International commodity markets determine these input costs, with prices fluctuating based on global supply-demand dynamics, energy costs, and geopolitical factors.
Raw material price increases squeeze profit margins unless companies can pass costs through to customers via higher selling prices. The ability to pass through costs depends on competitive dynamics, subsidy policy frameworks, and customer price sensitivity.
Regulatory and Policy Risks
Government subsidy policies significantly affect fertilizer industry economics. Subsidy rate changes, payment timing delays, or policy framework modifications can impact revenue realization and profitability. Companies must adapt to policy changes while managing business operations effectively.
Environmental regulations, safety requirements, and quality standards impose compliance costs and operational constraints. Regulatory complexity requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation to maintain compliance while managing costs.
Working Capital Requirements
The fertilizer business involves significant working capital needs related to raw material inventory, work-in-process, finished goods inventory, and trade receivables. Seasonal demand patterns create working capital cycles that peak during high consumption periods.
Subsidy payment timing affects receivables levels and cash flow patterns. Delays in subsidy releases from government increase working capital requirements and financing costs. Companies manage working capital through inventory optimization, credit management, and appropriate financing arrangements.
Competition and Market Share Dynamics
Competitive intensity affects pricing power and market share stability. New capacity additions, import competition, or aggressive competitor actions can pressure margins or market positions. Companies must continuously focus on operational efficiency and customer service to maintain competitive positioning.
Brand strength, distribution network depth, and customer relationships provide some insulation against competitive pressures. However, commodity fertilizer products face inherent competitive challenges given limited differentiation potential.
Financial Performance Historical Context
Multi-Year Trend Analysis
Evaluating company performance requires examining trends over multiple years rather than focusing solely on single-quarter results. Historical financial data provides context for assessing whether recent performance represents sustainable improvement or temporary favorable conditions.
Revenue trends over three-to-five-year periods indicate market position evolution and growth trajectory. Profit margin trends reveal operational efficiency changes and competitive positioning developments. Return metrics over extended periods demonstrate capital deployment effectiveness and business quality.
Seasonal Pattern Recognition
The fertilizer industry exhibits strong seasonal patterns aligned with agricultural cycles. Kharif season (monsoon crops) and Rabi season (winter crops) create distinct demand periods. Q1 (April-June) typically captures pre-monsoon and early Kharif season activity.
Comparing Q1 FY26 results with Q1 FY25 provides appropriate year-over-year assessment controlling for seasonal factors. However, investors should also examine sequential quarterly trends and full-year performance to understand complete business patterns.
Cyclical Business Characteristics
Fertilizer industry performance exhibits cyclical characteristics related to agricultural commodity price cycles, raw material cost cycles, and capacity addition waves. Understanding these cyclical patterns helps assess whether current performance reflects peak cycle conditions or sustainable trends.
Companies that maintain profitability across business cycles demonstrate stronger fundamental quality than those with highly cyclical earnings patterns. Capital discipline during favorable periods helps companies weather subsequent downturns.
Analyst Coverage and Market Views
Research Firm Assessments
Financial research firms and brokerage houses publish analysis and recommendations on publicly traded companies. JM Financial, among other research providers, maintains coverage of Paradeep Phosphates with periodic research reports evaluating financial performance, business prospects, and valuation.
Research reports typically include price targets representing analyst estimates of appropriate share value based on financial projections and valuation methodologies. Investors should note that price targets reflect analyst opinions rather than guaranteed outcomes, and actual performance may vary significantly from projections.
Earnings Estimate Revisions
Following quarterly results announcements, analysts revise their earnings estimates to reflect new information and updated assumptions. Significant results beats or misses relative to expectations often trigger estimate revisions that can influence stock price movements.
Consensus earnings estimates compiled from multiple analyst projections provide market expectation benchmarks. Comparing actual results to consensus estimates helps assess whether performance exceeded, met, or fell short of market expectations.
Sector Outlook Perspectives
Research analysts covering the fertilizer sector provide perspectives on industry trends, policy developments, and demand outlook. Sector reports examine factors including monsoon forecasts, government policy directions, raw material cost trends, and capacity dynamics.
Investors benefit from considering multiple analytical perspectives rather than relying on single sources. Different analysts may emphasize various factors or reach different conclusions based on their analytical frameworks and assumptions.
Investment Considerations
Valuation Context
Current market prices reflect collective investor assessments of company prospects, business quality, and appropriate valuation multiples. Comparing current valuations to historical ranges and peer company multiples provides context for assessing relative attractiveness.
Premium valuations relative to historical averages or peer companies suggest that markets expect superior growth, profitability, or business quality. Whether such premiums prove justified depends on actual future performance relative to expectations.
Growth Prospects Assessment
Long-term investment decisions require evaluating sustainable growth potential beyond near-term results. Growth drivers may include market share gains, capacity expansions, product portfolio enhancements, operational efficiency improvements, or favorable industry trends.
India’s agricultural development trajectory, including factors like irrigation expansion, crop intensification, and farming practice modernization, influences long-term fertilizer demand growth. Companies well-positioned to serve evolving agricultural needs may capture disproportionate growth opportunities.
Risk-Return Tradeoffs
Investment decisions involve balancing potential returns against associated risks. Higher-growth companies or premium-valued stocks may offer attractive return potential but typically involve greater uncertainty and volatility. Conservative investors may prefer companies with stable operations and modest valuations.
Portfolio diversification across sectors, market capitalizations, and risk profiles helps manage overall investment risk while maintaining return potential. Individual stock positions should be sized appropriately relative to total portfolio value and investor risk tolerance.
Stakeholder Perspectives
Shareholder Value Considerations
Existing shareholders evaluate whether company performance justifies continued ownership or whether rebalancing makes sense given changed circumstances. New potential shareholders assess whether current valuations offer attractive risk-adjusted return prospects.
Dividend policies, capital allocation decisions, and management’s strategic priorities affect shareholder value creation over time. Companies that consistently deliver on strategic objectives while maintaining financial discipline tend to reward long-term shareholders.
Agricultural Customer Impact
For farmers and agricultural customers, fertilizer product quality, availability, and pricing directly impact farming economics. Companies that maintain reliable supply, consistent quality, and responsive customer service build loyalty and sustainable business relationships.
Technical support services, agronomic guidance, and customized product solutions add value beyond basic fertilizer supply. Companies investing in customer relationships and service capabilities may achieve competitive advantages supporting long-term business sustainability.
Industry Ecosystem Relationships
Fertilizer companies operate within ecosystems including raw material suppliers, distribution partners, government agencies, and agricultural communities. Maintaining constructive relationships across the ecosystem supports operational effectiveness and business continuity.
Corporate social responsibility initiatives, sustainability commitments, and community engagement contribute to company reputation and social license to operate. These factors increasingly influence stakeholder perceptions and long-term business viability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What were the key financial metrics in Paradeep Phosphates’ Q1 FY26 results?
Paradeep Phosphates reported consolidated net profit of ₹255.8 crore for Q1 FY26 compared to ₹5.4 crore in Q1 FY25. Revenue from operations stood at ₹3,754 crore versus ₹2,377 crore in the year-ago quarter. EBITDA reached ₹466 crore with a margin of 12.4%, compared to ₹147 crore and 6.2% margin respectively in Q1 FY25. These figures are available in the company’s quarterly results filed with stock exchanges.
How did the stock price react to the quarterly results announcement?
Following the Q1 FY26 results release, Paradeep Phosphates shares traded in the range of ₹227-₹234 on BSE and NSE exchanges. Stock price movements around results announcements reflect market participants’ collective assessment of financial performance relative to expectations. Trading volumes and price volatility typically increase during such periods as investors process new information.
What is Paradeep Phosphates’ position in India’s fertilizer industry?
Paradeep Phosphates operates as a significant private sector producer of phosphatic fertilizers in India. The company manufactures products including DAP and various NPK grades at facilities in Paradeep (Odisha) and Zuari Nagar (Goa). The company competes in a sector that includes both private and public sector manufacturers serving India’s agricultural markets.
What factors influence profitability in the phosphatic fertilizer business?
Profitability in the phosphatic fertilizer business depends on multiple factors including raw material costs (phosphoric acid, ammonia, etc.), manufacturing efficiency, capacity utilization, product pricing, subsidy policy frameworks, and agricultural demand levels. Companies with efficient operations, favorable cost structures, and strong distribution networks typically maintain better profitability. Seasonal demand patterns and monsoon conditions significantly impact quarterly performance.
What are the main risks facing Paradeep Phosphates’ business?
Key risk factors include monsoon dependency and agricultural cycle volatility, raw material price fluctuations, competition intensity, government subsidy policy changes, working capital requirements, and seasonal demand variations. The company’s operations are subject to regulatory frameworks, environmental compliance requirements, and quality standards. Single-quarter results should be evaluated within the context of these risk factors and longer-term performance trends.
How do current valuation metrics compare to historical levels?
Based on the trading range around ₹220-₹230, the P/E ratio approximated 22-23 times, the price-to-book ratio stood around 4 times, and the three-year average ROE was approximately 14.4%. Investors typically evaluate these metrics relative to historical ranges, sector peer comparisons, and broader market valuations. Premium valuations relative to historical averages suggest market expectations for continued strong performance.
What is the significance of EBITDA margin expansion in Q1 FY26?
The EBITDA margin improvement to 12.4% in Q1 FY26 from 6.2% in Q1 FY25 indicates enhanced operational profitability relative to revenue. Margin expansion can result from economies of scale, operational efficiency improvements, favorable product mix, or effective cost management. Sustained margin improvements over multiple quarters provide stronger evidence of structural profitability enhancement versus temporary favorable conditions.
What role do government subsidies play in the fertilizer industry?
Government subsidies under the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) scheme significantly affect the economics of phosphatic fertilizer manufacturers. Subsidy programs aim to ensure fertilizer affordability for farmers while supporting domestic manufacturing. Subsidy rates, payment timing, and policy framework changes directly impact company revenues and cash flows. Companies must operate effectively within this policy framework while managing subsidy-related working capital requirements.
About the Author
Nueplanet
Senior Financial Markets Analyst
Nueplanet is a financial markets analyst specializing in coverage of India’s commodity and agricultural sectors. With the years of experience analyzing fertilizer industry dynamics, regulatory frameworks, and company financial performance, Nueplanet provides detailed examination of quarterly results, market trends, and investment considerations.
This analysis draws exclusively on publicly available information including stock exchange filings, company announcements, regulatory disclosures, and official government data. All financial figures cited are based on company filings with BSE and NSE stock exchanges or official press releases.
Editorial Commitment
This content provides factual analysis of publicly disclosed financial information and observable market data. The analysis examines multiple aspects of company performance, sector dynamics, and risk factors to enable informed reader assessment. No investment recommendations are provided, as individual investment decisions should be based on personal financial circumstances, risk tolerance, and professional consultation.
Information accuracy is prioritized through verification against official company filings, stock exchange disclosures, and regulatory databases. Financial metrics and ratios are calculated based on disclosed financial statements. Market data reflects publicly available trading information from recognized stock exchanges.
Published: July 29, 2025
Last Updated: July 29, 2025
Disclaimer: This article provides informational analysis based on publicly available data and does not constitute investment advice, stock recommendations, or offers to buy or sell securities. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Readers should conduct independent research and consult qualified financial advisors before making investment decisions. The author and publisher assume no liability for financial decisions made based on this content.
Source References:
- Company quarterly results filed with BSE/NSE
- Stock exchange price and volume data
- Public company disclosures and announcements
- Industry reports and government publications
Latest Posts
Our previous related articles include:
Helpful Resources
Paradeep Phosphates share price jumps nearly 13% to a record high post strong Q1 results 2025
Paradeep Phosphates jumps 17%, hits new high on multifold surge in Q1 profit
Q1 Results impact report includes Paradeep and peer movements






















Post Comment