
GNG Electronics Share Price: Full Story, Context, Outlook
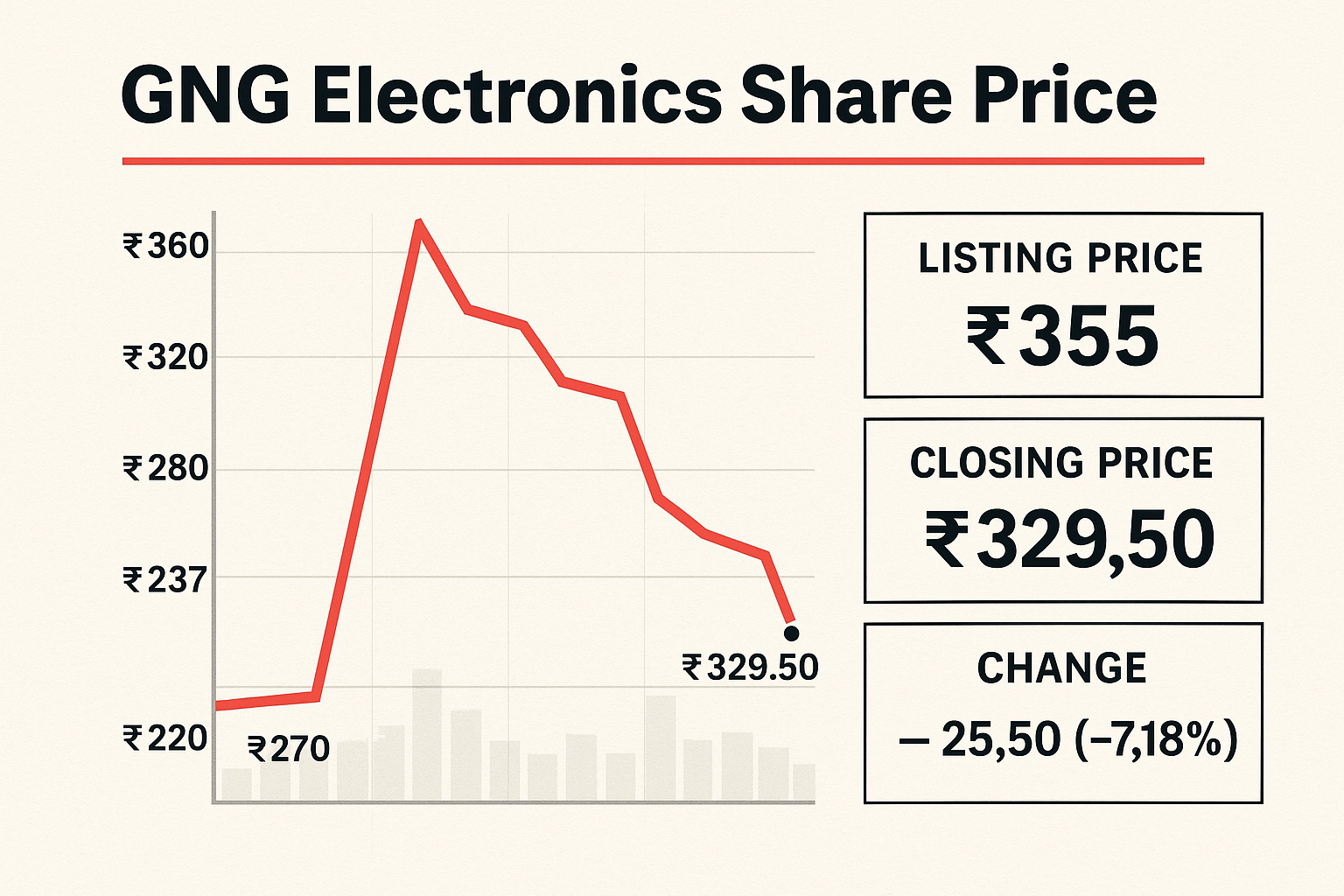
GNG Electronics (Electronics Bazaar) made a stellar market debut on July 30, 2025, listing at ₹355 on NSE—about 50% above its ₹237 IPO price. After initial exuberance, shares cooled and corrected by over 8%, settling near ₹325–₹340, sparking debate on whether to hold or book profits.
Table of Contents
Published: July 30, 2025
Last Updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
GNG Electronics Limited completed its initial public offering on July 30, 2025, marking a significant milestone in India’s refurbished technology sector. The company, which operates under the Electronics Bazaar brand, specializes in the refurbishment and sale of laptops, desktops, and information and communication technology devices.
The IPO attracted substantial investor interest across institutional, non-institutional, and retail categories. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the offering, including subscription data, pricing details, listing performance, business operations, financial metrics, and investment considerations.
The information presented is based on publicly available data from stock exchanges, regulatory filings, and official company disclosures. This analysis aims to help readers understand the company’s market position and evaluate its long-term prospects.
Overview of GNG Electronics Limited
Company Background and Operations
GNG Electronics Limited was established in 2006 as a refurbisher of information and communication technology devices. The company operates across multiple countries, serving both business and consumer markets. Its primary operations include sourcing used technology equipment, refurbishing these devices to meet quality standards, and selling them through various distribution channels.
The business model addresses demand for cost-effective technology solutions while contributing to environmental sustainability through device lifecycle extension. The company has developed operational capabilities across procurement, technical refurbishment, sales, and after-sales support.
GNG Electronics serves customers in India and international markets. The company has established relationships with corporate clients, retail consumers, and institutional buyers across different geographies.
Business Model and Service Portfolio
The company’s operations encompass several interconnected activities. Procurement involves sourcing used technology equipment from corporate clients, government entities, and other suppliers. The refurbishment process restores devices to functional condition through technical repairs, component replacement, and quality testing.
Sales channels include direct business-to-business transactions, retail stores, online platforms, and export markets. The company also operates buy-back programs where customers can return used devices for future credit. After-sales services include warranty support, technical assistance, and replacement options.
Environmental compliance services address electronic waste management requirements. The company handles disposal and recycling of components that cannot be refurbished, generating additional revenue from material recovery and compliance services.
Geographic Presence and Market Reach
GNG Electronics operates in 38 countries across multiple continents. In India, the company maintains a network of distribution channels covering major urban centers and smaller markets. The domestic market represents a significant portion of overall revenue.
International operations include the United States, where demand exists for affordable technology alternatives. European markets align with regional sustainability policies and circular economy initiatives. Operations in African countries address growing technology adoption in emerging economies.
The United Arab Emirates serves as a regional hub for Middle Eastern markets. This geographic diversification provides revenue stability and reduces dependence on any single market.
IPO Structure and Subscription Details
Offering Size and Price Band
The initial public offering comprised a total issue size of ₹460 crore. The company set a price band between ₹225 and ₹237 per share, with the final issue price determined at ₹237 per share. This pricing strategy balanced capital raising objectives with investor return expectations.
The IPO structure included both fresh issue of shares and offer for sale by existing shareholders. Proceeds from the fresh issue were designated for debt reduction, working capital requirements, and general corporate purposes.
The pricing reflected company valuations based on financial performance, growth projections, and market conditions at the time of the offering. Investment banks managing the IPO conducted extensive roadshows to institutional investors before finalizing the price.
Subscription Analysis by Category
The offering received significant oversubscription across all investor categories. Qualified institutional buyers, including mutual funds, insurance companies, and foreign portfolio investors, subscribed to 266 times the shares allocated to their category. This indicated strong institutional confidence in the company’s fundamentals.
Non-institutional investors, comprising high-net-worth individuals and corporate entities, subscribed to 226 times their allocation. This category typically includes sophisticated investors who conduct detailed due diligence before committing capital.
Retail individual investors subscribed to 47 times the shares allocated to their category. The retail participation reflected growing public interest in equity markets and awareness of the refurbished technology sector.
Overall, the IPO achieved 150.21 times total oversubscription, placing it among highly sought-after public offerings in recent Indian market history. The subscription levels exceeded initial expectations and indicated broad-based investor demand.
Pre-Listing Market Indicators
Before official listing, shares traded in the grey market, an unofficial platform where investors trade IPO shares before listing. Grey market premiums ranged between ₹90 and ₹100 above the issue price, suggesting potential gains of approximately 38 percent.
However, grey market indicators do not always accurately predict listing performance. Multiple factors, including overall market conditions, sector sentiment, and final allocation patterns, influence actual listing prices.
In this case, the actual listing performance exceeded grey market predictions, indicating stronger demand than anticipated through unofficial trading channels.
Listing Day Performance and Market Response
Opening Price and Initial Trading
GNG Electronics shares commenced trading on July 30, 2025, on both the National Stock Exchange and Bombay Stock Exchange. On NSE, shares opened at ₹355, representing a 49.8 percent premium over the issue price of ₹237. On BSE, the opening price was ₹350, delivering a 47.7 percent immediate gain.
The listing performance provided substantial returns to investors who received allocations in the IPO. The opening prices established an initial market capitalization of approximately ₹2,850 crore for the company.
Strong opening prices reflected the high oversubscription levels and positive investor sentiment toward the refurbished technology sector. Market participants viewed the company’s business model as aligned with sustainability trends and cost-conscious consumer behavior.
Trading Volume and Liquidity
The debut trading session generated significant market activity. Combined turnover across both exchanges reached approximately ₹887 crore, indicating active participation from traders and investors. Trading volume exceeded 2.6 crore shares on the first day.
High trading volumes provided liquidity for investors seeking to enter or exit positions. The activity demonstrated market confidence and price discovery efficiency during initial trading.
Intraday price movements ranged from a low of ₹325 to a high of ₹359. These fluctuations reflected normal profit-booking by short-term traders and fresh buying by longer-term investors.
Post-Listing Price Adjustment
Following initial gains, shares experienced a price correction of 8 to 10 percent during afternoon trading. Prices settled around ₹325.5 on NSE, representing a consolidation from opening levels.
Such corrections are common after strong IPO listings. Early investors and allottees often book profits after listing gains, creating selling pressure. Simultaneously, new investors assess valuation levels before entering positions.
Market analysts described this adjustment as healthy price discovery rather than fundamental weakness. The correction allowed the stock to find a more sustainable trading range after initial euphoria subsided.
Financial Performance Analysis
Revenue Growth and Operational Metrics
For the fiscal year ending March 2025, GNG Electronics reported revenue of ₹1,420 crore. This represented a 24 percent increase compared to the previous fiscal year. Revenue growth reflected increased sales volumes, geographic expansion, and market share gains.
The company’s revenue composition includes sales of refurbished devices, after-sales services, warranty programs, and e-waste management fees. Diversified revenue streams provide stability and reduce dependence on any single income source.
Operating margins ranged between 7 and 9 percent during the fiscal year. These margins reflected the company’s cost structure, including procurement costs, refurbishment expenses, distribution costs, and administrative overheads.
Profitability and Bottom-Line Performance
Net profit for FY25 reached ₹69 crore, representing 32 percent growth year-over-year. Profit growth exceeded revenue growth, indicating improving operational efficiency and margin management.
The profit margin improvement resulted from several factors. Scale advantages in procurement reduced per-unit costs. Operational efficiencies in refurbishment processes improved throughput. Geographic expansion into higher-margin markets contributed to overall profitability.
However, the company continued to invest in expansion initiatives, technology infrastructure, and working capital requirements. These investments temporarily constrained profit margins but supported long-term growth objectives.
Return Ratios and Capital Efficiency
Return on equity, which measures profitability relative to shareholder equity, stood at approximately 35 percent. This metric exceeded industry averages and demonstrated effective capital utilization. High ROE indicates the company generates substantial returns for each unit of shareholder investment.
Return on capital employed, measuring returns on all capital invested in the business, reached approximately 20 percent. This ratio assesses how efficiently the company uses both equity and debt capital to generate profits.
Asset turnover ratios indicated effective inventory management and operational efficiency. In working capital-intensive businesses like refurbishment, managing inventory levels and collection cycles significantly impacts overall returns.
Valuation Metrics and Market Comparisons
At the listing price, shares traded at approximately 39 times FY25 earnings. Some analysts calculated higher multiples based on market capitalization and profit figures. These valuations incorporated growth expectations and market leadership position.
Valuation multiples reflected premium pricing compared to traditional retail or technology services companies. However, comparisons with international refurbishment companies and circular economy businesses suggested the multiples were within reasonable ranges given growth prospects.
The price-to-earnings ratio would compress if the company maintained earnings growth momentum. Conversely, slower growth or margin pressure could make current valuations appear stretched.
Capital Structure and Debt Management
Existing Debt Levels and Borrowing Costs
GNG Electronics carried debt of approximately ₹320 to ₹330 crore on its balance sheet before the IPO. This borrowing supported working capital requirements, inventory procurement, and operational expansion. Interest expenses on this debt reduced net profitability.
The company’s debt-to-equity ratio indicated moderate leverage. While debt provided growth capital, high interest costs and financial risk concerned some investors. Credit ratings reflected the company’s ability to service debt obligations.
Management identified debt reduction as a priority for IPO proceeds utilization. Reducing leverage would improve financial flexibility and reduce vulnerability to interest rate fluctuations.
Post-IPO Capital Allocation Plans
The company announced plans to use IPO proceeds for debt reduction during FY26. Retiring existing borrowings would eliminate associated interest expenses, directly improving net profit margins. Lower debt levels would also strengthen balance sheet ratios.
Improved financial metrics could lead to better credit ratings, reducing future borrowing costs. Enhanced financial flexibility would support strategic initiatives without relying on external financing.
Additional IPO proceeds would support working capital requirements as the business scales. Procurement of inventory requires significant capital investment, particularly during expansion phases.
Working Capital Management Considerations
The refurbishment business model requires substantial working capital. The company must purchase used equipment before refurbishing and selling it. This creates a time lag between cash outflow and cash inflow.
Effective working capital management involves optimizing inventory levels, managing supplier payment terms, and accelerating customer collections. Inefficient working capital utilization ties up capital and reduces overall returns.
The company’s cash conversion cycle, measuring the time between cash outflow and cash inflow, remains an important metric for assessing operational efficiency. Improvements in this cycle enhance cash flow generation and reduce financing needs.
Market Position and Competitive Landscape
Industry Leadership and Market Share
GNG Electronics positions itself as India’s largest organized player in the ICT refurbishment sector. The company has developed scale advantages through processing volumes and supplier relationships. These advantages provide cost benefits unavailable to smaller competitors.
Market share calculations in the refurbished technology sector remain challenging due to the presence of unorganized players. However, the company’s revenue scale and client relationships suggest a leading position in the organized segment.
First-mover advantages in developing a comprehensive service platform create competitive barriers. Newer entrants must invest significantly to replicate similar capabilities across procurement, refurbishment, distribution, and after-sales support.
Customer Base and Revenue Concentration
The company serves over 4,100 corporate clients across various sectors. This client base provides revenue diversification and reduces dependence on any single customer relationship. Corporate clients typically require larger volumes and value consistent quality standards.
However, revenue concentration analysis reveals that approximately 47 percent of revenue comes from the top 10 customers. This concentration creates vulnerability to contract losses or renegotiations. Losing a major client could significantly impact financial performance.
The company continues efforts to expand its customer base and reduce concentration risks. Balanced growth across existing clients and new customer acquisition remains important for sustainable revenue development.
Supplier Relationships and Procurement Dynamics
Procurement sourcing shows similar concentration patterns. Approximately 57 percent of procurement depends on the top 10 suppliers. This concentration creates supply chain risks if major suppliers reduce availability or increase prices.
Strong supplier relationships provide consistent inventory access and favorable pricing terms. However, over-reliance on limited suppliers could create vulnerabilities during supply disruptions or supplier consolidation.
The company works to diversify its supplier network while maintaining strategic partnerships with key providers. Balancing supplier relationships with diversification objectives remains an ongoing priority.
Competitive Threats and Industry Evolution
The refurbished technology sector continues to evolve with changing market dynamics. Growing market size attracts new competitors, including well-funded startups and established technology retailers expanding into refurbishment.
Competition could pressure profit margins through pricing competition. However, GNG’s established operations, brand recognition, and scale advantages provide defensive characteristics against new entrants.
Technology evolution presents both opportunities and challenges. Rapid product cycles create supply of used equipment for refurbishment but also require continuous adaptation of technical capabilities.
Risk Factors and Investment Considerations
Business and Operational Risks
Customer concentration represents a significant business risk. High revenue dependence on major clients creates vulnerability if key relationships deteriorate or contracts are not renewed. The company must continuously deliver value to maintain these strategic relationships.
Supplier concentration poses procurement risks. Limited supplier options could result in higher costs, inventory shortages, or supply disruptions. Geographic and supplier diversification helps mitigate these risks.
Working capital intensity constrains financial flexibility. Significant capital requirements for inventory procurement limit available resources for other strategic initiatives. Efficient working capital management becomes critical for sustainable growth.
Technology obsolescence creates ongoing challenges. Rapid technology evolution requires continuous adaptation of refurbishment capabilities. The company must invest in training, equipment, and processes to handle newer device generations.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Environmental regulations governing electronic waste continue to evolve. Stricter compliance requirements create both costs and opportunities. The company must invest in compliant disposal processes while potentially generating revenue from responsible recycling services.
Operating across 38 countries exposes the company to multiple regulatory environments. Each jurisdiction has specific requirements for technology refurbishment, waste management, and business operations. Compliance complexity increases with geographic expansion.
Changes in import-export regulations, taxation policies, or trade barriers could impact cross-border operations. The company must monitor regulatory developments and adapt operations accordingly.
Market and Economic Risks
Demand for refurbished technology correlates with economic conditions. Economic downturns could reduce corporate technology spending while potentially increasing consumer demand for cost-effective alternatives. Understanding these dynamics helps assess economic sensitivity.
Currency fluctuations impact international operations. The company conducts transactions in multiple currencies, creating foreign exchange exposure. Currency movements affect procurement costs, sales revenue, and overall profitability.
Sector-specific trends influence business performance. Growing sustainability awareness supports demand for refurbished products. Conversely, declining new technology prices could reduce the price advantage of refurbished devices.
Valuation and Market Risks
Current valuation multiples reflect growth expectations and market leadership. If the company fails to meet growth expectations or faces operational challenges, valuations could compress significantly. Investors must assess whether current prices adequately reflect both opportunities and risks.
Market sentiment toward IPOs and technology stocks influences trading performance. Broader market corrections or sector-specific concerns could negatively impact stock performance regardless of company fundamentals.
Lock-in expiration for pre-IPO shareholders could create selling pressure when restrictions end. Increased supply of shares in the market may temporarily depress prices.
Expert Analysis and Recommendations
Analyst Perspectives on Valuation
Prashanth Tapse from Mehta Equities noted that the listing performance met expectations while highlighting premium valuations. The analysis suggested that conservative investors consider booking profits while long-term investors focus on the company’s scalability potential.
Shivani Nyati from Swastika Investmart recommended partial profit realization for investors who received IPO allocations. The analysis suggested implementing stop-loss orders near ₹280 to manage downside risks. Long-term investors with higher risk tolerance could maintain positions while monitoring execution quality.
Yash Chauhan from INVasset PMS expressed optimism about future prospects contingent on margin improvement and operational execution. The analysis viewed the price-to-earnings ratio as reasonable given growth potential, suggesting investors consider building positions after observing quarterly performance.
Anand Rathi Securities highlighted first-mover advantages in the business-to-business refurbishment segment while noting working capital challenges. The analysis recommended a balanced approach combining partial profit-booking with selective holdings based on execution assessment.
Investment Strategy Considerations
Conservative investors might consider booking profits on listing gains while maintaining smaller positions for potential long-term upside. This approach prioritizes capital preservation while retaining exposure to growth opportunities.
Growth-oriented investors could maintain larger positions while monitoring quarterly results and operational metrics. This strategy requires tolerance for short-term volatility and confidence in the company’s execution capabilities.
Long-term institutional investors should evaluate the company within broader technology and sustainability investment themes. Assessment should include management quality, competitive positioning, and market expansion capabilities.
All investment strategies should incorporate regular portfolio reviews and willingness to adjust positions based on changing fundamentals or market conditions.
Key Performance Indicators to Monitor
Investors should track several metrics in coming quarters. Revenue growth rates indicate market demand and competitive positioning. Maintaining or expanding profit margins demonstrates operational efficiency and pricing power.
Customer acquisition and retention rates show the company’s ability to grow its client base while maintaining existing relationships. Changes in customer concentration levels affect risk profile.
Working capital metrics, including inventory turnover and cash conversion cycles, indicate operational efficiency. Improvements in these areas enhance cash flow generation and reduce financing requirements.
Debt reduction progress according to stated plans demonstrates management’s commitment to financial discipline. Interest coverage ratios show the company’s ability to meet debt obligations comfortably.
Growth Opportunities and Strategic Initiatives
Geographic Expansion Potential
The company operates in 38 countries but maintains opportunities for deeper penetration in existing markets and entry into new geographies. Emerging markets with growing technology adoption present significant expansion potential.
Each geographic market has unique characteristics regarding regulatory environment, competitive dynamics, and customer preferences. Successful expansion requires adapting operations while maintaining quality standards and cost efficiency.
International expansion provides revenue diversification and reduces dependence on the domestic Indian market. However, it also increases operational complexity and requires investment in local capabilities.
Product and Service Diversification
The current focus on laptops, desktops, and ICT devices could expand to include smartphones, tablets, wearables, and other consumer electronics. Diversification would increase the addressable market and provide additional growth avenues.
Service enhancement opportunities include financing options for customers, insurance products, and extended warranty programs. These services could increase customer lifetime value and generate recurring revenue streams.
Development of enterprise solutions, including device lifecycle management services for corporate clients, represents another growth opportunity. Comprehensive service offerings differentiate the company from competitors focused solely on device sales.
Technology and Operational Innovation
Investment in digital platforms could enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. E-commerce capabilities expand market reach beyond physical distribution networks.
Artificial intelligence applications in inventory management, pricing optimization, and quality assessment could improve margins and operational effectiveness. Data analytics help identify market trends and customer preferences.
Sustainability initiatives, including advanced recycling technologies and carbon footprint reduction, could create competitive advantages while addressing environmental concerns. These initiatives align with growing corporate and consumer focus on sustainability.
Sector Outlook and Industry Trends
Circular Economy and Sustainability Trends
The global shift toward circular economy principles supports long-term demand for refurbished technology. Governments and corporations increasingly prioritize sustainability in procurement decisions.
Environmental awareness among consumers grows, particularly in developed markets. Younger demographics show higher acceptance of refurbished products compared to previous generations.
Regulatory pressures to reduce electronic waste create favorable conditions for refurbishment businesses. Extended producer responsibility regulations in various countries mandate proper device lifecycle management.
Technology Adoption in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets demonstrate rapid technology adoption but face affordability challenges. Refurbished devices provide cost-effective access to technology for educational institutions, small businesses, and price-sensitive consumers.
Government digitalization initiatives in developing countries create demand for affordable technology solutions. Refurbished devices can help bridge the digital divide by making technology accessible to broader populations.
However, emerging market operations also present challenges including payment collection, infrastructure limitations, and varying quality expectations.
Competitive Dynamics and Industry Consolidation
The refurbishment sector remains fragmented with numerous small players alongside a few organized companies. Industry consolidation could occur as larger players acquire smaller competitors or as unorganized players struggle to meet regulatory requirements.
Technology companies increasingly recognize refurbishment as complementary to new product sales. Original equipment manufacturers may expand their certified refurbishment programs, creating both competition and partnership opportunities.
E-commerce platforms increasingly feature refurbished products, providing additional distribution channels but also intensifying online competition.
Macroeconomic Factors and Market Context
Interest Rate Environment and Financing Costs
Interest rate policies by central banks affect both corporate borrowing costs and consumer purchasing power. Lower interest rates reduce financing expenses and support higher consumer spending.
The company’s planned debt reduction reduces sensitivity to interest rate fluctuations. However, future borrowing costs for expansion initiatives depend on prevailing rate environments.
Consumer financing options for purchasing refurbished devices become more attractive in lower interest rate environments, potentially supporting sales growth.
Currency Movements and International Operations
Foreign exchange rate fluctuations impact the company’s international operations. Procurement in foreign currencies creates cost variability depending on rupee movements against major currencies.
Sales revenue from international markets also faces currency exposure. Natural hedging occurs when procurement and sales occur in the same currency, but this doesn’t apply across all operations.
Currency hedging strategies can mitigate foreign exchange risks but involve costs and complexity. Management must balance hedging expenses against risk reduction benefits.
Technology Sector Trends and New Product Cycles
New product launches by technology manufacturers create supply of previous-generation devices for refurbishment. Rapid product cycles in smartphones and laptops provide consistent inventory availability.
However, declining prices of new technology products could reduce the price advantage of refurbished alternatives. The company must maintain sufficient price differentials to attract cost-conscious buyers.
Technology adoption rates in various segments influence demand patterns. Enterprise technology refresh cycles create bulk procurement opportunities, while consumer demand shows more seasonal variation.
Comparison with Industry Peers
Domestic Market Competitors
The Indian refurbished technology market includes both organized and unorganized players. Organized competitors typically focus on specific segments or geographic regions. GNG’s comprehensive service platform and national presence differentiate it from specialized competitors.
Unorganized players often compete primarily on price with limited quality assurance or after-sales support. These players create pricing pressure but typically serve different customer segments with lower service expectations.
Traditional retailers expanding into refurbished products bring brand recognition but may lack specialized refurbishment expertise. These competitors could gain market share through established distribution networks.
International Refurbishment Companies
International refurbishment companies operate in mature markets with different competitive dynamics. These companies provide benchmarks for operational efficiency, service capabilities, and profitability metrics.
Valuation comparisons with international peers help assess whether GNG trades at premium, discount, or comparable multiples. Differences in growth rates, market conditions, and operational models affect appropriate valuation levels.
International expansion by foreign refurbishment companies into India could introduce well-funded competition with established operational expertise. However, local market knowledge and relationships provide defensive advantages.
Technology Services and IT Asset Management Companies
Technology services companies offering IT asset management services represent adjacent competitors. These companies may provide device lifecycle management without specialized refurbishment capabilities.
IT asset management companies serve corporate clients with comprehensive technology solutions. Partnerships between refurbishment specialists and IT service providers could create value for both parties.
The competitive landscape continues evolving as boundaries between different technology service categories blur. Companies increasingly offer integrated solutions combining multiple capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contributed to the strong IPO subscription levels?
The IPO received 150.21 times total oversubscription due to several factors. The company’s position as India’s largest organized ICT refurbisher attracted investor interest. Financial performance showing 24 percent revenue growth and 32 percent profit growth demonstrated operational momentum. The circular economy business model aligned with sustainability trends. Operations across 38 countries provided geographic diversification. Institutional investors viewed the offering as exposure to an emerging sector with growth potential.
How does customer concentration impact business risk?
Approximately 47 percent of revenue derives from the top 10 customers, creating concentration risk. Loss of a major client could significantly impact financial performance. However, the company serves over 4,100 total clients, providing diversification beyond major accounts. Corporate clients typically sign multi-year contracts, offering revenue visibility. The company continues expanding its customer base to reduce concentration levels over time. Investors should monitor changes in customer concentration metrics in future quarters.
What role will debt reduction play in improving profitability?
The company plans to reduce borrowings of ₹320 to ₹330 crore using IPO proceeds. Debt reduction will eliminate associated interest expenses, directly improving net profit margins. Lower leverage ratios will strengthen balance sheet metrics and potentially improve credit ratings. Enhanced financial flexibility will support growth investments without relying on external financing. Reduced financial risk should improve investor confidence. The debt reduction timeline extends through FY26 according to management statements.
How sustainable is the current valuation given growth expectations?
Shares trade at approximately 39 times FY25 earnings at the listing price. This valuation reflects premium pricing for growth prospects and market leadership position. Sustainability depends on the company meeting growth expectations and improving profit margins. If revenue growth continues at 20-25 percent annually and margins improve, the valuation multiple could compress to more reasonable levels. However, slower growth or operational challenges could make current valuations appear stretched. Investors should evaluate quarterly performance against growth assumptions.
What competitive advantages support market leadership?
GNG Electronics benefits from several competitive advantages. Scale in procurement provides cost advantages unavailable to smaller competitors. Relationships with over 4,100 corporate clients create revenue stability and switching costs. Comprehensive service capabilities from procurement through disposal differentiate the company from specialized competitors. International operations across 38 countries provide geographic diversification. First-mover advantages in organized refurbishment created brand recognition and operational expertise. Quality standards and warranty programs build customer trust.
How do working capital requirements affect financial performance?
The refurbishment business model requires substantial working capital for inventory procurement. The company must purchase used equipment before refurbishing and selling it, creating cash flow timing differences. Effective working capital management involves optimizing inventory levels and collection cycles. Inefficient working capital utilization reduces overall returns and may require external financing. The cash conversion cycle, measuring time between cash outflow and inflow, remains a critical metric. Improvements in working capital efficiency enhance cash generation and reduce financing needs.
What macroeconomic factors could impact future performance?
Several macroeconomic variables influence business performance. Economic growth rates affect corporate technology spending and consumer purchasing power. Currency fluctuations impact international operations and procurement costs. Interest rate changes affect both financing expenses and customer demand. Regulatory developments in e-waste management create compliance costs but also service opportunities. Technology sector trends influence product availability and pricing dynamics. Geographic diversification across 38 countries provides some protection against localized economic challenges.
Should investors consider this stock for long-term holdings?
Long-term investment appeal depends on individual risk tolerance and objectives. The company operates in a growing market supported by sustainability trends and technology adoption in emerging markets. Strong operational metrics and market leadership provide competitive advantages. Exposure to the circular economy theme aligns with environmental priorities. However, investors must consider concentration risks, working capital intensity, and premium valuations. Success depends on execution of debt reduction, margin improvement, and geographic expansion plans. Conservative investors might maintain smaller positions, while growth-oriented investors could hold larger allocations subject to ongoing performance monitoring.
Summary and Conclusion
GNG Electronics Limited’s initial public offering in July 2025 generated significant investor interest, resulting in 150.21 times total oversubscription. The listing on July 30, 2025, delivered substantial returns with opening prices representing approximately 50 percent premiums over the issue price.
The company operates as India’s largest organized player in the ICT refurbishment sector with presence across 38 countries. Business operations encompass procurement, refurbishment, sales, after-sales support, and e-waste management services. For FY25, the company reported revenue of ₹1,420 crore with 24 percent growth and net profit of ₹69 crore with 32 percent growth.
The investment thesis centers on market leadership in an emerging sector, geographic diversification, and alignment with circular economy trends. However, investors must evaluate concentration risks, working capital requirements, premium valuations, and execution capabilities. Management plans to use IPO proceeds for debt reduction, which should improve profitability metrics.
Market analysts provided mixed recommendations ranging from profit-booking to long-term holding based on individual risk profiles. The stock’s performance following listing will depend on quarterly execution, competitive dynamics, and broader market conditions.
Investors should monitor revenue growth rates, profit margins, customer acquisition trends, working capital efficiency, and debt reduction progress in coming quarters. The company’s ability to execute expansion plans while maintaining quality standards and customer relationships will determine long-term investment returns.
About the Author
Nueplanet
Nueplanet is a financial markets analyst specializing in equity research, IPO analysis, and technology sector coverage. With the years of experience in financial journalism and investment analysis, Nueplanet provides detailed, factual coverage of market developments.
This analysis is based on publicly available information from stock exchange filings, regulatory disclosures, company announcements, and official financial statements. The goal is to provide readers with comprehensive, verified information to support informed investment decisions.
All data and statistics referenced in this article are sourced from official channels including stock exchange websites, Securities and Exchange Board of India filings, company investor presentations, and regulatory announcements. The author maintains independence and does not have any financial interest in the companies covered.
Commitment to Accuracy: This content is regularly updated to reflect the latest verified information. Readers should verify all information independently and consult qualified financial advisors before making investment decisions.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice, recommendation, or solicitation. The author is not a registered investment advisor. Readers should conduct independent research and consult qualified financial professionals before making investment decisions. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Investments in equity markets carry risk including potential loss of principal.
Helpful Resources
For further reading and reference, see these external analyses and news coverage:
Shares tumble over 8% after listing; should you buy, sell or hold?
Mint coverage: IPO listing, valuation & analyst perspectives
Latest Posts
Here are previous posts from our site for further investor insights (just titles mentioned):
- TS EAMCET Phase‑2 Seat Allotment 2025
- Asian Paints Share Price
- Maharashtra HSC Result 2025 Declared
- Varun Beverages Share Price
- NSDL IPO & Share Price
Conclusion
GNG Electronics has delivered a high‑visibility IPO debut, offering investors nearly 50% listing gains within a day. Yet, stocks rarely rise straight—post‑listing correction of ~8% reflects short‑term volatility. Based on robust business fundamentals, global footprint, and sustainable model, long‑term investors may find value, provided execution aligns with expectations and balance sheet strength improves. Conservative investors may choose to crystallise early gains while keeping a portion for future upside.






















Post Comment