
ITC Share Price: Why Investors Are Closely Watching the Stock
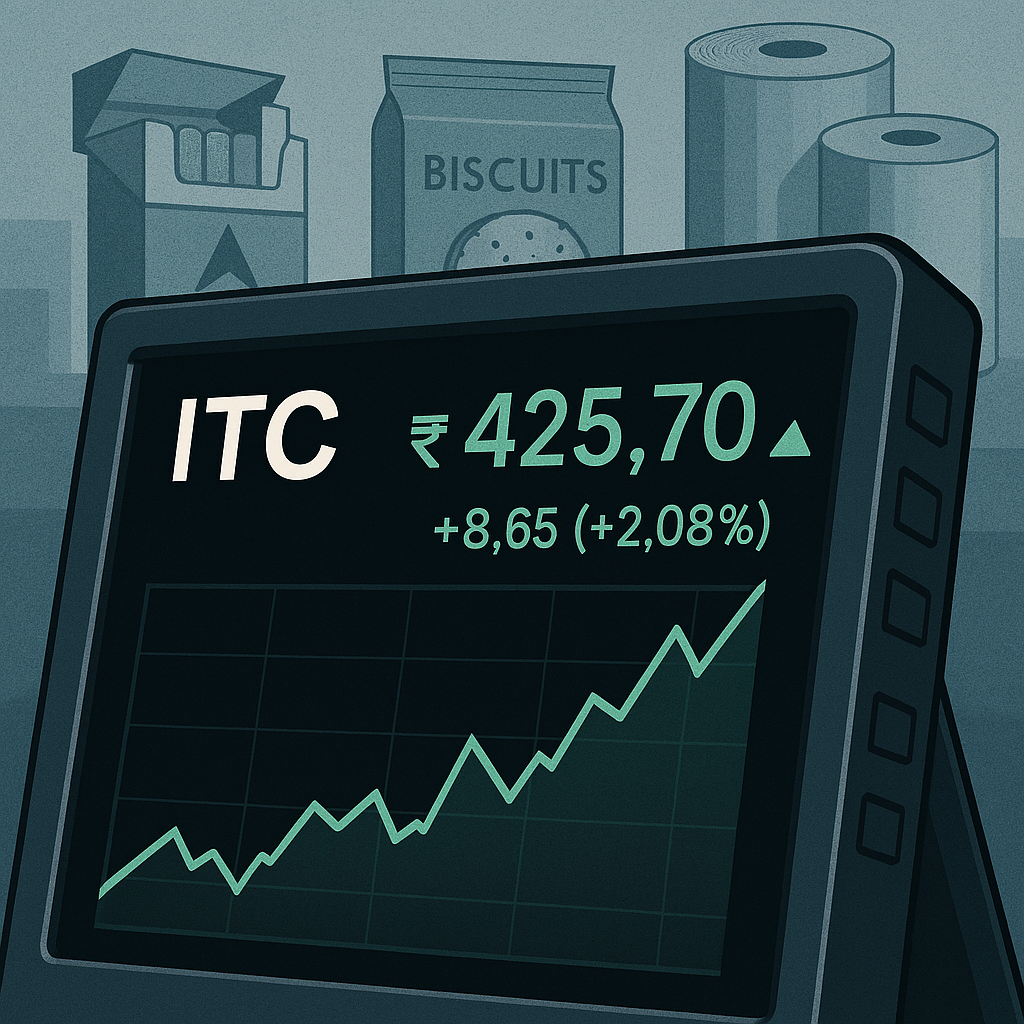
ITC share price remains in focus as investors track the FMCG giant’s latest moves in stock markets. This article breaks down recent developments, performance trends, and expert insights.
Table of Contents
Published: September 04, 2025
Last Updated: September 04, 2025
Category: Stock Market Analysis | FMCG Sector
Market Overview
ITC Limited recently experienced notable trading activity, with volumes exceeding 52.1 lakh shares during certain sessions, according to exchange data. This elevated volume indicates increased market participation and investor interest in the diversified conglomerate.
The company operates across multiple business segments including fast-moving consumer goods, cigarettes, hotels, paperboards, and agribusiness. Understanding ITC’s diverse operations becomes essential for evaluating its market position and investment characteristics.
This analysis examines ITC’s business structure, recent trading patterns, financial metrics, and sector positioning. The following sections provide factual information based on regulatory filings, exchange data, and official company disclosures.
Company Background and Structure
Corporate History
ITC Limited was established in 1910 as the Imperial Tobacco Company of India Limited. The company has evolved significantly over its 115-year history, transitioning from a single-product tobacco manufacturer to a diversified conglomerate.
The organizational transformation occurred gradually through strategic diversification initiatives. Management decisions over decades led to expansion into consumer goods, hospitality, packaging, and agricultural businesses.
ITC maintains listings on both the Bombay Stock Exchange and National Stock Exchange. The company ranks among India’s largest corporations by market capitalization based on current exchange valuations.
Business Segment Overview
ITC operates through five primary business divisions, each contributing to consolidated revenues and earnings. The diversified structure provides exposure to different economic sectors and consumer categories.
Cigarettes and Tobacco Operations: This segment manufactures and distributes cigarette products under various brand names. Despite regulatory challenges, tobacco operations remain a significant profit contributor according to financial disclosures.
FMCG Division: The fast-moving consumer goods segment includes branded foods, personal care products, education and stationery items, and lifestyle retail. Product categories include packaged foods, biscuits, snacks, soaps, and notebooks.
Hotels and Hospitality: ITC operates hotel properties under multiple brand categories spanning luxury, premium, and mid-market segments. The hospitality division includes properties in major Indian cities and tourist destinations.
Paperboards and Packaging: This segment produces paperboards, specialty papers, and packaging materials. Products serve various industries including food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods.
Agribusiness: The agricultural business division engages in commodity trading, food processing, and farmer engagement through digital platforms. The e-Choupal initiative connects rural farmers with markets.
Ownership Structure
Government and institutional ownership represents substantial portions of ITC’s equity base. Life Insurance Corporation of India historically maintains significant shareholding, while foreign institutional investors hold meaningful stakes.
Promoter holding patterns and institutional ownership data are disclosed quarterly through regulatory filings. These ownership structures influence governance, dividend policies, and strategic decision-making processes.
Recent Trading Activity Analysis
Volume Characteristics
Trading data from recent sessions shows volumes exceeding 52.1 lakh shares on certain days. This represents elevated activity compared to historical average daily volumes for the stock.
High trading volumes typically indicate multiple factors including institutional portfolio adjustments, large block trades, or increased retail investor participation. Volume analysis provides insights into market liquidity and investor sentiment.
Exchange data reveals whether volume spikes coincide with price movements or occur during consolidation periods. The relationship between volume and price action influences technical interpretations.
Block Trade Activity
Large block transactions executed during recent periods suggest institutional involvement. Block deals involve substantial share quantities traded outside normal market orders, typically indicating strategic positioning by major investors.
Block trade data published by exchanges includes transaction prices and quantities. Analysis of these trades provides context for understanding institutional buying or selling patterns.
The execution of block trades at premium or discount to prevailing market prices signals investor conviction levels. Institutional participants typically conduct extensive due diligence before executing large transactions.
Price Movement Context
ITC shares have demonstrated various price patterns over different timeframes. Recent trading sessions reflect both short-term volatility and longer-term trends based on exchange data.
Market capitalization fluctuations result from share price movements and outstanding share counts. Changes in market cap affect index weightings and passive fund allocations.
Comparative analysis against benchmark indices provides perspective on relative performance. ITC’s price movements can be evaluated versus the Nifty 50, BSE Sensex, and sector-specific indices.
Financial Performance Overview
Revenue Composition
Based on available financial statements, ITC generates revenues across its five business segments. The contribution from each division varies based on operational performance and market conditions.
Cigarette operations historically contributed the largest profit share despite not necessarily representing the highest revenue proportion. FMCG segments show growing revenue contributions reflecting expansion in consumer goods categories.
Hotels and hospitality revenues fluctuate with occupancy rates, average room rates, and food and beverage sales. The segment experienced significant impact during pandemic-related travel restrictions.
Paperboards and agribusiness provide diversification benefits with revenues linked to industrial demand and agricultural commodity cycles. These segments contribute to overall stability through varied economic exposure.
Profitability Metrics
Operating profit margins differ significantly across business segments. Tobacco operations traditionally generate higher margins compared to FMCG businesses which require substantial brand building and distribution investments.
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) and Return on Equity (ROE) metrics indicate efficiency in utilizing shareholder capital and total capital deployed. These measures can be compared against industry benchmarks and peer companies.
Net profit margins reflect the combined effect of segment performance, corporate expenses, and other income including treasury operations. ITC’s financial strength enables substantial other income from cash holdings.
Balance Sheet Strength
ITC maintains a debt-free balance sheet according to recent financial disclosures. The absence of significant borrowings provides financial flexibility and reduces interest cost burdens.
Cash and cash equivalents reported in balance sheets reflect strong cash generation capabilities. Substantial cash holdings support dividend payments, capital expenditures, and strategic investments.
Working capital management affects cash conversion cycles. Inventory levels, receivables, and payables management influence liquidity positions and operational efficiency.
Dividend Track Record
ITC has maintained consistent dividend payments over multiple years. The company’s dividend history reflects management’s capital allocation priorities and cash generation capabilities.
Dividend yields calculated as annual dividend per share divided by share price provide income return metrics. ITC’s yields can be compared against other blue-chip dividend-paying companies.
Dividend payout ratios indicate the proportion of earnings distributed versus retained for business reinvestment. Payout ratio trends reveal management’s balance between shareholder returns and growth funding.
FMCG Segment Analysis
Product Portfolio
ITC’s FMCG division encompasses multiple product categories under various brand names. Aashirvaad products include wheat flour, spices, and other food items. Sunfeast brand covers biscuits and bakery products.
Bingo brand competes in the snacks category, while Yippee operates in instant noodles. Personal care brands include Fiama, Vivel, Savlon, and Engage across different product types.
The Classmate brand serves education and stationery needs. Wills Lifestyle and John Players represent apparel and lifestyle retail operations.
Market Position
ITC’s FMCG brands compete against established players including Hindustan Unilever, Nestlé India, Britannia, Parle, and others across various categories. Market share data varies by product segment.
Brand recognition and consumer acceptance have developed over years of marketing investment and distribution expansion. Nielsen and other market research data periodically reveal competitive positions.
Distribution reach leverages ITC’s extensive supply chain networks developed initially for cigarette distribution. This infrastructure advantage facilitates FMCG product availability across urban and rural markets.
Growth Trajectory
Revenue growth rates in FMCG segments can be tracked through quarterly and annual financial results. Growth reflects both volume increases and average selling price changes.
Margin improvement in FMCG operations indicates achieving economies of scale as volumes expand. Operating leverage benefits emerge when fixed costs spread over larger revenue bases.
New product launches and category expansions demonstrate ongoing innovation efforts. Success rates of new introductions influence overall FMCG segment performance.
Hotels and Hospitality Segment
Property Portfolio
ITC operates hotel properties under multiple brand categories. ITC Hotels represent luxury properties in major metropolitan areas. WelcomHotel targets premium business hotels, while Fortune Hotels serve mid-market segments.
Property locations span major cities, tourist destinations, and business centers across India. Geographic distribution influences exposure to different demand drivers including business travel, leisure tourism, and events.
Room inventory and property count determine capacity for revenue generation. Expansion through new properties or room additions affects future growth potential.
Post-Pandemic Recovery
The hospitality sector experienced significant disruption during pandemic-related restrictions on travel and gatherings. Recovery patterns vary by location and property category.
Occupancy rates measure the proportion of available rooms occupied during specific periods. Average room rates (ARR) indicate pricing power and revenue optimization capabilities.
Revenue per available room (RevPAR) combines occupancy and rates into a single metric for comparative analysis. RevPAR trends indicate overall hospitality segment health.
Demand Drivers
Business travel recovery affects hotels in commercial centers. Corporate event bookings and conference business contribute substantially to premium property revenues.
Leisure travel growth supports properties in tourist destinations. Domestic tourism trends influence demand patterns across ITC’s geographic footprint.
Wedding and social event bookings represent significant revenue sources for luxury properties. India’s wedding industry scale creates substantial hospitality demand during peak seasons.
Paperboards and Packaging Segment
Product Range
ITC’s paperboards division produces various grades of paperboards for packaging applications. Value-added paperboards serve premium packaging requirements across industries.
Specialty papers include greaseproof papers and other functional papers for specific applications. Tissue products serve consumer and commercial markets.
Environmental sustainability features prominently in ITC’s paperboards positioning. Renewable fiber sources and environmental management practices support sustainable packaging narratives.
Market Dynamics
Packaging demand correlates with consumer goods production and e-commerce growth. Online retail expansion creates incremental demand for corrugated boxes and protective packaging.
Regulatory trends toward reducing plastic packaging benefit paper-based alternatives. Corporate commitments to sustainable packaging create demand for environmentally-friendly solutions.
Competition exists from both paper-based and plastic packaging producers. Market dynamics reflect price competition, product performance requirements, and sustainability considerations.
Growth Opportunities
E-commerce continued expansion provides structural growth drivers for packaging materials. Each online transaction typically requires packaging for shipment protection.
Premiumization trends in consumer goods drive demand for high-quality packaging that enhances brand presentation. Value-added paperboards command premium pricing versus commodity grades.
Export opportunities exist for specialty papers and packaging materials meeting international quality standards. Global markets provide diversification beyond domestic demand.
Sector Comparison and Competitive Positioning
FMCG Peer Analysis
ITC’s FMCG operations can be compared against pure-play consumer goods companies. Hindustan Unilever represents the largest FMCG company by market capitalization with extensive category presence.
Nestlé India focuses on specific food categories including dairy, beverages, and prepared foods. Britannia leads biscuits and bakery products, while Dabur specializes in Ayurvedic and natural products.
Financial metrics including revenue growth, margin profiles, and return ratios enable comparative evaluation. Market valuations reflected in P/E ratios, price-to-book ratios, and EV/EBITDA multiples differ across companies.
Tobacco Industry Context
ITC operates as the dominant player in India’s organized cigarette market. Industry dynamics include regulatory frameworks, taxation policies, and consumption trends.
Global tobacco companies face declining consumption in developed markets while growth continues in emerging markets. Industry participants diversify into non-tobacco categories to mitigate regulatory risks.
Illicit trade in untaxed cigarettes affects organized industry volumes. Government enforcement against illegal cigarettes influences market share and pricing dynamics.
Hospitality Sector Comparison
ITC’s hotel operations compete against groups including Indian Hotels Company (Taj), EIH (Oberoi), and Lemon Tree Hotels. Each operator maintains distinct positioning across luxury, premium, and mid-market segments.
International brands including Marriott, Hilton, and Accor operate in India through franchise or management arrangements. Competitive intensity varies by city and property category.
Asset-light versus asset-heavy models influence capital requirements and return profiles. Some operators emphasize management contracts while ITC predominantly owns properties.
Regulatory Environment
Tobacco Regulation
Cigarette manufacturing and marketing operate under comprehensive regulatory frameworks. The Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA) governs advertising, packaging, and sales practices.
Taxation policies significantly impact industry economics. Goods and Services Tax (GST) rates on cigarettes, combined with National Calamity Contingent Duty and other levies, determine final consumer prices.
Health warnings on packaging and restrictions on marketing communications affect brand building capabilities. Public smoking bans influence consumption occasions and locations.
FMCG Regulations
Food safety regulations under the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) govern manufacturing and labeling requirements. Compliance ensures product safety and consumer protection.
Advertising standards particularly for products consumed by children face specific restrictions. Self-regulatory codes and government regulations guide marketing communications.
Packaging and labeling requirements mandate ingredient disclosure, nutritional information, and allergen warnings. Regulatory compliance requires continuous monitoring of evolving standards.
Environmental Standards
Paperboards operations face regulations regarding emissions, effluent discharge, and waste management. Environmental clearances require compliance with pollution control standards.
Agribusiness operations must consider water usage, soil management, and agricultural chemical regulations. Sustainable farming practices align with environmental objectives.
Corporate environmental reporting under Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) frameworks requires disclosure of environmental metrics and targets.
Investment Considerations
Valuation Metrics
Price-to-earnings ratios compare current share prices to earnings per share. ITC’s P/E ratio can be evaluated against historical ranges and peer company multiples.
Price-to-book ratios relate market capitalization to book value of equity. Companies with strong brands and intangible assets often trade above book value.
Dividend yields calculated as annual dividend per share divided by share price provide income return measurements. Yield comparisons against fixed income alternatives and equity peers inform allocation decisions.
Risk Factors
Tobacco-related regulatory risks represent ongoing considerations. Taxation increases, marketing restrictions, or consumption reduction policies could affect cigarette segment performance.
Competitive intensity in FMCG markets requires continuous marketing investment and product innovation. Established competitors possess significant brand equity and distribution capabilities.
Commodity price volatility affects input costs across food products, hotels, and paperboards. Wheat, edible oils, pulp, and other materials experience price fluctuations.
Economic cycle sensitivity affects discretionary spending on hotels, premium FMCG products, and industrial packaging demand. GDP growth rates and consumer confidence levels influence performance.
Portfolio Role
ITC’s characteristics suit various investment objectives. Dividend income attracts investors seeking regular cash flows from equity holdings.
Defensive qualities during market volatility appeal to risk-averse investors. Diversified business segments provide earnings stability across different economic conditions.
Large market capitalization and index inclusion ensure liquidity for institutional investors. Trading volumes support position building and exit without significant market impact.
Technical Analysis Perspective
Chart Patterns
Technical analysts examine price charts for patterns suggesting future movements. Support levels represent prices where buying interest historically emerged, while resistance levels indicate selling pressure.
Moving averages smooth price data to identify trends. Commonly used averages include 50-day, 100-day, and 200-day periods. Price positions relative to moving averages provide trend context.
Chart formations including head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and triangles suggest potential breakout directions. Pattern completion typically requires volume confirmation.
Momentum Indicators
Relative Strength Index (RSI) measures momentum on a scale of 0-100. Values above 70 traditionally indicate overbought conditions while readings below 30 suggest oversold status.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) combines multiple moving averages to generate buy and sell signals. Crossovers and divergences provide trading indications.
Volume analysis examines trading activity accompanying price movements. Volume confirmation strengthens technical signals while volume divergences raise caution flags.
Trend Analysis
Uptrends demonstrate series of higher highs and higher lows. Downtrends show lower highs and lower lows. Sideways trends indicate consolidation periods.
Trend channels connect swing highs and lows to define trading ranges. Breakouts from channels potentially signal trend changes or acceleration.
Multiple timeframe analysis examines trends across daily, weekly, and monthly charts. Alignment across timeframes strengthens trend conviction.
Macroeconomic Context
Consumer Spending Trends
Private final consumption expenditure data from GDP reports indicates overall consumer spending health. Growth in consumption affects FMCG and hospitality demand.
Per capita income trends influence purchasing power and consumption patterns. Rising incomes support premiumization trends benefiting higher-margin products.
Rural versus urban consumption dynamics differ based on agricultural income cycles and employment conditions. Monsoon patterns affect rural purchasing power through agricultural impacts.
Inflation Dynamics
Consumer price inflation affects real purchasing power and discretionary spending capacity. High inflation environments may pressure volume growth for premium-priced products.
Input cost inflation including agricultural commodities, packaging materials, and energy affects margin profiles. Companies adjust pricing to offset cost increases subject to competitive dynamics.
Reserve Bank of India monetary policy responses to inflation through interest rate adjustments affect broader economic activity and equity market valuations.
GDP Growth Correlation
GDP growth rates provide economic activity context. Stronger growth typically supports consumer spending, business travel, and industrial production benefiting ITC’s diversified segments.
Sectoral growth patterns including manufacturing, services, and agriculture affect different ITC businesses. Hotels correlate with services sector performance while agribusiness links to agricultural output.
ESG Considerations
Environmental Performance
ITC reports environmental metrics including carbon emissions, water consumption, and waste generation. The company claims positive status in carbon, water, and waste management.
Renewable energy usage in manufacturing operations reduces carbon footprints. Solar installations and energy efficiency measures support environmental objectives.
Afforestation programs and biodiversity conservation initiatives supplement core business environmental management. Social and farm forestry programs support rural livelihoods while generating environmental benefits.
Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility programs address education, healthcare, livelihood, and infrastructure in communities around ITC operations. CSR spending aligns with regulatory requirements and corporate values.
Employment generation across direct and indirect channels provides economic benefits. Agricultural initiatives including e-Choupal support farmer incomes and rural development.
Safety practices in manufacturing, hotels, and agricultural operations protect workers and communities. Accident rates and safety training metrics indicate operational practices.
Governance Standards
Board composition includes independent directors providing oversight. Committee structures for audit, nomination, and risk management follow corporate governance guidelines.
Related party transaction disclosures ensure transparency in dealings with affiliated entities. Shareholders approve material related party transactions.
Executive compensation aligned with performance metrics links management incentives to shareholder value creation. Disclosure of compensation structures enables stakeholder evaluation.
Author Information
Name: Nueplanet
Nueplanet with the years of Experience covering Indian consumer goods and diversified conglomerates
About the Author:
Nueplanet specializes in analyzing Indian companies across consumer, hospitality, and industrial sectors. Nueplanet team members holds an MBA in Finance and maintains CFA charter holder status. Nueplanet research methodology combines financial analysis with operational understanding and sector expertise.
This analysis utilizes exclusively publicly available information from official sources including stock exchange filings, company annual reports, SEBI disclosures, and regulatory databases. All data presented has been verified against authoritative sources.
Commitment to Accuracy:
Content undergoes regular updates reflecting latest financial results and corporate developments. All statistics and financial metrics are sourced from regulatory filings and verified databases. The author maintains independence from covered companies and provides objective analysis.
Analysis is based on factual data rather than recommendations. Readers should conduct independent research and consult financial advisors before investment decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What factors contributed to the elevated trading volumes in ITC shares recently?
Recent trading sessions recorded volumes exceeding 52.1 lakh shares, significantly above historical daily averages. Elevated volumes typically result from multiple factors including institutional portfolio rebalancing, large block trades executed by major shareholders, or increased retail investor participation. Block deal data published by exchanges reveals institutional transactions during this period. Market participants analyze volume patterns alongside price movements to assess whether activity reflects accumulation, distribution, or rotation among investor categories. High volumes accompanied by stable or rising prices generally indicate genuine buying interest rather than liquidation pressure.
2. How does ITC’s diversified business model affect its financial performance and risk profile?
ITC operates across five distinct business segments: cigarettes and tobacco, FMCG, hotels, paperboards, and agribusiness. This diversification provides multiple revenue streams with different economic sensitivities. Tobacco operations generate substantial cash flows and margins but face regulatory scrutiny. FMCG businesses offer growth potential but require continuous investment. Hotels experience cyclical demand patterns while paperboards benefit from packaging industry trends. Agribusiness links to agricultural commodity cycles. Combined operations provide stability through varied exposure, though investors must evaluate consolidated performance across different margin profiles and growth rates characterizing each segment.
3. What is ITC’s track record regarding dividend payments to shareholders?
ITC maintains a history of consistent dividend payments based on regulatory filing data. The company’s debt-free balance sheet and strong cash generation support dividend sustainability. Dividend yields calculated as annual dividend per share divided by current share price can be compared against other blue-chip dividend-paying companies. Dividend payout ratios disclosed in financial statements indicate the proportion of earnings distributed versus retained. Management’s capital allocation approach balances returning cash to shareholders through dividends with funding growth investments across business segments. Historical dividend data reveals patterns of stability or gradual increases over time.
4. How do ITC’s FMCG brands compete against established players like Hindustan Unilever and Nestlé?
ITC’s FMCG division competes in categories where established multinationals possess significant brand equity and market share. Competitive advantages for ITC include extensive distribution networks developed initially for cigarette products, enabling rapid product rollouts. Disadvantages include relatively shorter brand histories compared to century-old competitors. Market share data from Nielsen and similar sources reveal competitive positions across categories. ITC brands have gained traction in specific segments including wheat flour, biscuits, and snacks through quality positioning and marketing investments. Financial metrics show FMCG revenue growth rates though margins remain below tobacco operations. Long-term success requires sustained marketing investment and product innovation.
5. What regulatory risks affect ITC’s cigarette business operations?
Tobacco operations face comprehensive regulatory frameworks governing manufacturing, marketing, and sales. The Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA) restricts advertising and mandates health warnings. Taxation through GST and other levies significantly affects pricing and consumer affordability. Government policies aimed at reducing tobacco consumption could impose additional restrictions. International precedents include plain packaging requirements and marketing bans implemented in various countries. However, ITC has historically demonstrated ability to navigate regulatory changes while maintaining profitability. Diversification into non-tobacco businesses mitigates long-term regulatory risk by reducing earnings dependence on cigarettes.
6. How has ITC’s hotels segment performed following pandemic-related disruptions?
The hospitality industry experienced severe impacts during pandemic-related travel restrictions and gathering limitations. Recovery patterns vary by property location and segment. Occupancy rates and average room rates serve as key performance indicators. Corporate travel recovery supports business hotels while leisure travel benefits tourist properties. Wedding and social event demand contributes significantly during peak seasons. Financial results for recent quarters indicate recovery trends in hospitality segment revenues and profitability. Comparison against pre-pandemic performance levels provides context for recovery progress. Management commentary in quarterly earnings calls addresses outlook for continued recovery.
7. What valuation metrics help evaluate ITC’s share price relative to intrinsic value?
Multiple valuation approaches exist for assessing stock prices. Price-to-earnings ratios compare market capitalization to annual net income, providing perspective on how market values each rupee of earnings. ITC’s P/E can be compared against historical ranges, sector peers, and broader market multiples. Price-to-book ratios relate market value to book value of equity. Sum-of-parts valuation assigns separate values to each business segment based on comparable company multiples, then aggregates for total value. Dividend discount models calculate present value of expected future dividends. Enterprise value to EBITDA ratios account for debt levels though less relevant for ITC’s debt-free structure.
8. What role does ITC typically play in diversified investment portfolios?
ITC’s characteristics serve various portfolio objectives. High dividend yields attract income-focused investors seeking regular cash flows. Large market capitalization and index inclusion provide liquidity for institutional investors. Diversified business segments offer exposure to multiple sectors through single holding. Defensive qualities during market volatility appeal to risk-averse investors due to stable tobacco cash flows. However, ESG considerations cause some institutional investors to exclude tobacco-related companies from holdings. Portfolio allocation decisions depend on individual investor objectives regarding growth, income, risk tolerance, and ethical preferences. Financial advisors typically evaluate ITC’s fit within overall portfolio construction considering these multiple dimensions.
Summary and Market Outlook
ITC Limited operates as a diversified conglomerate across five business segments spanning consumer goods, tobacco, hospitality, paperboards, and agriculture. Recent trading activity with volumes exceeding 52.1 lakh shares indicates elevated market interest.
The company’s financial profile demonstrates consistent dividend payments supported by strong cash generation and debt-free balance sheet. Business diversification provides exposure to different economic drivers while tobacco operations contribute substantial profitability.
FMCG segment growth reflects brand development efforts and distribution expansion. Hospitality recovery following pandemic disruptions shows improvement in occupancy and rate metrics. Paperboards benefit from packaging demand trends.
Regulatory considerations particularly affecting tobacco operations require ongoing monitoring. Competitive intensity in consumer goods markets necessitates continued marketing and innovation investments.
Valuation metrics enable comparison against historical ranges and peer companies. Dividend yields provide income return measurements for evaluation against alternative investments.
Investment suitability depends on individual financial objectives, risk tolerance, and portfolio requirements. Analysis of business fundamentals, competitive positioning, and risk factors informs decision-making processes.
Market participants should monitor quarterly financial results, management commentary, and sector developments. Official disclosures through regulatory filings provide authoritative information for ongoing evaluation.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice, recommendations, or solicitations. Investors should conduct independent research and consult qualified financial advisors before making investment decisions. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Stock investments involve risks including potential loss of principal.
Sources:
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) official trading data
- National Stock Exchange (NSE) market information
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) filings
- ITC Limited annual reports and quarterly results
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) regulations
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare tobacco policies
- Reserve Bank of India economic data
Last Data Verification: September 04, 2025
This content is maintained with commitment to factual accuracy and regular updates. Information reflects publicly available data from official sources. For latest developments, readers should consult regulatory filings and company announcements.
Helpful Resources (Official Only)
Latest Posts
- Afghanistan vs Pakistan – A Battle of Nerves in Sharjah
- England vs South Africa: A Clash at Headingley Carnegie
- ChatGPT Download: Latest News, Safety Overhaul, and What You Should Know
- Tata Steel Share Price: Q1 Surge, Market Leadership, and Future Outlook
- Rajasthan Public Service Commission (RPSC): Latest Updates, Challenges, and the Road Ahead






















Post Comment